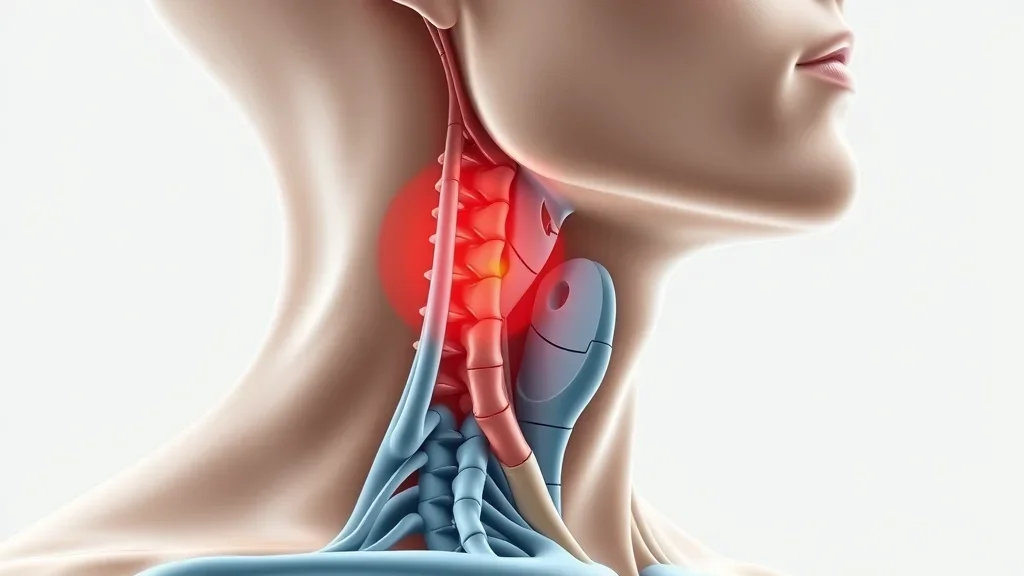
Did you know thyroglossal duct cysts affect up to 7% of the population? Understanding this common congenital neck cyst can lead to timely diagnosis and treatment, preventing complications and ensuring better health outcomes. Let’s uncover the essential facts together.What is a Thyroglossal Duct Cyst?A thyroglossal duct cyst is the most frequent congenital neck mass found in children, and it can appear in adults too. These cysts develop from a leftover tract called the thyroglossal duct, which forms when the thyroid gland moves to its final position in the neck during early development. If any portion of the duct remain as a child grows, it can fill with fluid and form a cyst. Understanding what is a thyroglossal duct cyst? is crucial for both accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.While these cysts are typically painless, they can become problematic if infected or if they grow large enough to impact breathing or swallowing. Timely identification and intervention are key to preventing complications, highlighting the need for public and professional awareness about this common—but often misunderstood—condition.Understanding the Prevalence of Thyroglossal Duct CystsThyroglossal duct cysts are a prevalent cause of neck masses in children and can account for up to 70% of congenital neck cysts. However, adults are not immune; recent studies show that 15-20% of cases are diagnosed in adulthood, typically presenting as a lump in the midline of the neck. These cysts can also be mistaken for other types of neck masses, which underscores the importance of thorough evaluation by healthcare professionals. Awareness of their prevalence aids in early screening, particularly in pediatric populations.The occurrence of these duct cysts makes them an integral part of clinical examination for neck swelling. Most cases present in early childhood, but they can appear at any age if an upper respiratory infection or other triggers cause the cyst to enlarge. Public education and education among health workers are crucial to decreasing delays in diagnosis, especially since a seemingly minor neck lump can sometimes progress to severe infection or even airway compromise if untreated.Why Knowing "What is a Thyroglossal Duct Cyst?" Matters for Timely DiagnosisRecognizing what is a thyroglossal duct cyst? can lead to more accurate, prompt diagnosis and a much better prognosis. These cysts often manifest as a small, movable neck lump that may go unnoticed until it causes discomfort or infection. Children are more likely to develop a thyroglossal duct cyst, but adults with unexplained midline neck masses should also be evaluated for this condition.Early detection is essential for optimal outcomes. Lack of awareness could lead to misdiagnosis, leaving the cyst untreated and potentially resulting in significant complications like infection or even the development of a rare carcinoma. As Dr. Sonia Patel, ENT specialist, notes:"Thyroglossal duct cysts are one of the most common neck cysts in children, but adults can be affected too. Early detection is crucial for optimal outcomes." – Dr. Sonia Patel, ENT specialistWhat You'll Learn About Thyroglossal Duct CystsDefinition and anatomy of thyroglossal duct cystsCommon symptoms and signsDiagnostic process and imaging testsTreatment options and proceduresPotential complications and preventionExpert insights and factsThyroglossal Duct Cyst OverviewAnatomy: The Thyroglossal Duct and Its RoleThe thyroglossal duct is a narrow canal formed during early embryonic development. It serves as the pathway along which the thyroid gland descends from its origin at the base of the tongue to its ultimate position in the lower neck. Normally, this duct disappears before birth, but if any portion remains, it can become a problem later in life. These persistent portions of the duct are the sites where a thyroglossal duct cyst may develop.Anatomically, these cysts are usually located in the midline, near the hyoid bone or just above the thyroid cartilage. The proximity to important neck structures, such as the airway and swallowing tract, makes the identification and management of these cysts especially important. Familiarity with this duct and its usual path in the neck is key to distinguishing thyroglossal duct cysts from other neck masses, including lymph nodes, branchial cleft cysts, and dermoid cysts.Formation and Development of Duct CystsThe formation of a thyroglossal duct cyst results from the failure of the thyroglossal duct to regress completely after the thyroid gland reaches its final position in the neck. Instead, a portion of the duct remains, creating the possibility for a cystic mass to form at any point along the duct’s original pathway. This is why the cyst often presents centrally in the neck, commonly just below the hyoid bone.External triggers, such as an upper respiratory infection, can cause the residual duct tissues to become inflamed and enlarge, leading to the visible and palpable neck mass associated with thyroglossal duct cysts. Understanding this embryological process is essential, not just for accurate diagnosis, but also for planning the best approach to treatment, which typically involves complete removal of the cyst and the entire tract to prevent recurrence.Comparison of Congenital Neck MassesFeatureThyroglossal Duct CystBranchial Cleft CystDermoid CystLocationMidline (often near hyoid bone), moves with swallowing/tongue outLateral neck, anterior to sternocleidomastoidMidline or lateral, usually submental/submandibularOriginRemnant of thyroglossal ductRemnant of branchial apparatusTrapped epithelial tissues in developmentSymptomsPainless lump, can become infected; may cause difficulty swallowingPainless lump, may become infected; rarely affects breathing/swallowingPainless, slow growing, rarely infectedTypical Age of PresentationChildhood or young adulthoodChildhood/adolescenceEarly childhoodRecognizing the Symptoms of a Thyroglossal Duct CystIdentifying the symptoms of a thyroglossal duct cyst is vital for early intervention. The classic sign is a midline neck lump that moves upward when the patient swallows or sticks out their tongue. Other symptoms may include difficulty swallowing, mild pain, redness or tenderness if infected, and a history of upper respiratory infections that might trigger the cyst to swell. These symptoms are essential clues for physicians conducting a physical examination of any neck mass.Midline neck lumpDifficulty swallowing or breathingRedness or tendernessHistory of upper respiratory infectionsOlder children and adults may notice the lump especially after a bout of upper respiratory illness. If infection occurs, the overlying skin can appear red or tender, increasing the risk of abscess formation if untreated. Recurrent neck masses, or those causing new swallowing or breathing difficulty, should always be evaluated by a healthcare provider. As Dr. Elaine Munroe, Pediatrician, states:"A painless, movable neck swelling that rises when swallowing or sticking out the tongue is almost pathognomonic for thyroglossal duct cyst." – Dr. Elaine Munroe, PediatricianIt's important to note that neck lumps in children can have several causes, and distinguishing between conditions like thyroglossal duct cysts and other sources of throat or neck swelling—such as tonsillitis—can be challenging. For a closer look at the symptoms and treatment options for another common pediatric neck condition, explore what causes tonsillitis in kids and how it’s managed.Diagnosis: How is a Thyroglossal Duct Cyst Identified?Diagnosis begins with a detailed physical examination, focusing on the characteristic findings: a well-defined, mobile, midline neck mass that moves on swallowing or tongue protrusion. However, confirmation relies on imaging and sometimes tissue sampling. The diagnostic journey ensures correct differentiation from other neck masses and helps delineate the cyst’s relationship with critical structures like the thyroid gland.Often, the diagnosis is clinical, but radiological and sometimes pathological assessment may be needed to exclude malignancy or other unusual presentations. The ultimate goal is accurate, safe, and effective management that minimizes recurrence or complications.Imaging Tests: Ultrasound, CT Scan, and MRI for Thyroglossal Duct CystsImaging plays an essential role in confirming a thyroglossal duct cyst and excluding other causes of neck swelling. Ultrasound is usually the first-line investigation, allowing visualization of the cyst, its location, and its relation to the thyroid tissue. If further evaluation is required—especially in adults or in recurrent or atypical cases—a CT scan or MRI can provide detailed anatomical maps, guide surgical planning, and help assess for complications like infection or possible carcinoma.These imaging tools not only clarify the diagnosis but can also reveal if normal thyroid tissue is present and functioning, ensuring that surgery does not compromise essential thyroid function. Radiological evidence, supplemented by clinical expertise, guarantees the best approach to individualized patient care.Role of Fine Needle Aspiration and BiopsyFine needle aspiration (FNA) may sometimes be advised if there is uncertainty about the diagnosis or if malignancy is suspected in a long-standing or atypically presenting duct cyst. Using a thin needle and image guidance, doctors can extract cells from the cyst for microscopic analysis. This test helps differentiate benign from malignant outcomes and can provide culture results if infection is present.While not required for every patient, FNA and biopsy offer peace of mind—particularly for adults or in cases where the cyst does not exhibit textbook features. Together with imaging and clinical assessment, these tools ensure the thyroid gland and all relevant neck tissues are thoroughly evaluated before any major intervention.Treatment & Management of Thyroglossal Duct CystsThe gold standard for thyroglossal duct cyst treatment is complete surgical removal. A specialized operation called the Sistrunk procedure is widely recognized as the safest and most effective way to ensure the cyst does not return. Medical therapy, such as antibiotics, may be used initially if the cyst is infected, but definitive treatment is always surgical.Optimal management includes not just removal of the cyst but also ablation of the entire tract—including a portion of the hyoid bone and all associated duct tissue—to minimize the risk of recurrence. This approach is essential for both children and adults to guarantee lasting results and a low rate of complications.The Sistrunk Procedure: Gold Standard for Duct Cyst RemovalThe Sistrunk procedure involves surgical excision of the cyst, the entire thyroglossal duct, and a central piece of the hyoid bone. This comprehensive removal is crucial because failure to remove every portion of the duct increases the odds of recurrence. The operation is performed under general anesthesia, usually through a small incision in the neck, and is considered a safe and highly effective surgery with minimal side effects when conducted by an experienced surgeon.Post-operatively, patients usually experience a rapid recovery, minimal pain, and a low recurrence rate. The Sistrunk procedure is now the worldwide gold standard; non-surgical approaches or simple cyst drainage without full tract removal are NOT recommended, as they frequently lead to repeat cyst formation. As Dr. Mark Jensen, Head & Neck Surgeon, explains:"The Sistrunk procedure has a high success rate and is considered the standard of care for treating thyroglossal duct cysts." – Dr. Mark Jensen, Head & Neck SurgeonRecovery, Prognosis, and Recurrence RatesRecovery from the Sistrunk procedure is typically smooth. Most patients can return to normal activities within a week, and wound healing is uneventful in the majority of cases. The risk of post-operative infection is low, especially with adherence to post-op care instructions. Recurrence rates are minimized—well below 5%—when the full tract, cyst, and a segment of the hyoid bone are removed.Patients are advised to follow up with their surgeon for regular check-ins and wound assessment after the operation. In rare instances, complications such as bleeding, infection, or nerve injury may occur, but these are greatly reduced with expert surgical care and thorough preoperative planning.Potential Complications of Untreated Thyroglossal Duct CystsWhen a thyroglossal duct cyst remains untreated, it can progress to serious complications. The most common issue is infection, which can lead to abscess formation—a collection of pus that requires urgent intervention. Occasionally, a chronic infected cyst can lead to the development of a fistula, or abnormal channel, to the skin surface.Infection and abscess formationFistula developmentRare risk of carcinomaThough uncommon, there’s a small risk (less than 1%) of carcinoma developing in a long-standing thyroglossal duct cyst. Persistent or recurrent symptoms, rapid cyst growth, or suspicious changes in clinical behavior should prompt urgent evaluation and possible biopsy. These potential outcomes highlight the necessity for early diagnosis and definitive treatment of all thyroglossal duct cysts.Prevention, Follow-up, and Patient EducationWhile congenital in nature and therefore not preventable, early recognition of thyroglossal duct cysts leads to the best health results. Patient education about the warning signs—such as a new midline neck lump, especially in children, or lumps that move with swallowing—can empower parents and patients to seek timely care. Regular follow-up ensures post-surgical success and minimizes recurrence.For those with a history of surgery, regular wound inspection and follow-up imaging may be scheduled to confirm complete healing and absence of new cyst formation. Teaching families to watch for recurrence or infection is important for long-term wellbeing.Tips for Early Recognition and Timely Intervention- Inspect any new, persistent midline neck swelling in children and adults. - If the lump moves with swallowing or sticking out the tongue, request prompt evaluation. - Seek medical advice if experiencing pain, redness, or signs of infection. - Do not ignore lumps that seem painless or non-tender—many early cysts are asymptomatic. - Complete removal using the Sistrunk procedure is key to preventing recurrence.Case Study: Successful Management of a Thyroglossal Duct CystA 9-year-old girl presented with a painless neck lump that her parents noticed moved each time she swallowed or stuck her tongue out. An ultrasound revealed a cystic midline mass just above her hyoid bone, with an otherwise normal thyroid gland. A Sistrunk procedure was performed: the cyst, tract, and a portion of the hyoid bone were removed. She recovered fully within a week, with no recurrence during 18 months of follow-up. This case highlights the importance of early identification and expert surgical management of thyroglossal duct cysts.Her story demonstrates the classic features—midline, mobile, painless lump—and confirms that with proper diagnosis and the Sistrunk procedure, children can return to normal life quickly and recurrence can be virtually eliminated.Clear, animated explanation of thyroglossal duct cysts for patients: illustrating what a thyroglossal duct cyst is, showing normal anatomy, how the cyst forms, and basic treatment options, with smooth transitions and friendly, simple visuals for patient education.People Also AskHow serious is a thyroglossal cyst?Although most thyroglossal duct cysts are benign, they can become infected, cause discomfort, or lead to complications like fistula formation or, rarely, malignancy if left untreated.What is the cause of thyroglossal duct cysts?Thyroglossal duct cysts arise when tissue along the route of the embryological thyroglossal duct fails to regress completely, creating a cystic cavity.How do you treat a thyroglossal duct cyst?The primary treatment is surgical removal via the Sistrunk procedure, along with antibiotics if infection is present.Can a thyroglossal duct cyst affect thyroid function?Thyroglossal duct cysts rarely affect thyroid function directly, but proper diagnostic imaging is required to confirm the presence of normal thyroid tissue.This video presents a real patient’s journey from diagnosis to post-op recovery, offering a detailed look at what to expect if you or your child need the Sistrunk procedure for a thyroglossal duct cyst.Frequently Asked Questions about Thyroglossal Duct CystsAre thyroglossal duct cysts hereditary?Most thyroglossal duct cysts result from developmental anomalies and are not hereditary.Can adults develop thyroglossal duct cysts?Yes. While most cases are seen in children, adults can present with thyroglossal duct cysts, sometimes after years of being asymptomatic.What is the recurrence rate after surgery?With proper Sistrunk procedure, recurrence rates are low, usually under 5%.Is hospitalization required for the Sistrunk procedure?Most patients require a brief hospital stay (often just one night for observation), but discharge is often possible the same day if no complications arise.Key Takeaways on What is a Thyroglossal Duct Cyst?Thyroglossal duct cysts are common congenital neck cysts that may present at any age.Prompt diagnosis allows successful surgical management.The Sistrunk procedure results in low recurrence and excellent prognosis.Summary and Next StepsReady to learn more about neck health? Explore our expert-reviewed resources or book a consultation with a certified ENT specialist today.If you’re interested in understanding how neck and throat health connects to broader digestive wellness, you may find it valuable to explore the landscape of esophageal disorders and their impact on adults. Gaining insight into these related conditions can help you take a more proactive approach to your overall well-being and recognize early warning signs beyond the neck.For a comprehensive overview and practical guidance, visit our resource on navigating the challenges of esophageal disorders for health-conscious adults. Expanding your knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions and support lifelong throat and digestive health.Early recognition and reliable surgical management offer excellent outcomes for patients with thyroglossal duct cysts. Stay informed, seek expert care, and prioritize regular follow-up for lifelong health.Referenceshttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470188/https://www.statpearls.com/ArticleLibrary/viewarticle/26402https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2003/0901/p885.htmlA thyroglossal duct cyst is a congenital neck mass resulting from the incomplete closure of the thyroglossal duct during embryonic development. This duct serves as the pathway for the thyroid gland’s descent from the base of the tongue to its final position in the neck. When portions of this duct persist, they can form cysts anywhere along this path, commonly presenting as midline neck lumps near the hyoid bone. (en.wikipedia.org)These cysts are typically painless but can become problematic if infected or enlarged, potentially leading to difficulty swallowing or breathing. They are the most common congenital neck masses, accounting for up to 70% of such cases, and are usually diagnosed in children, though they can also appear in adults. (pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)Diagnosis often involves a physical examination, where the cyst may move upward when the patient swallows or protrudes their tongue. Imaging studies like ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI are utilized to confirm the diagnosis and assess the cyst’s relationship with surrounding structures. (childrenshospital.org)The standard treatment is surgical removal through the Sistrunk procedure, which involves excising the cyst along with a portion of the hyoid bone and the entire thyroglossal tract to minimize recurrence. This procedure has a high success rate and is considered the gold standard for treating thyroglossal duct cysts. (childrens.com)For a visual understanding from the Mayo Clinic of the Sistrunk procedure, you may find the following video informative:Sistrunk Procedure for Excision of a Thyroglossal Duct Cyst

 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment