
Ever stopped and wondered: Is your pounding head truly a migraine—or could it be a tension headache masquerading as one?
Both migraine headaches and tension headaches are among the most common types of head pain, yet distinguishing between these two headache disorders can be challenging. Understanding the migraine headache vs tension headache location differences is critical for fast relief and choosing the right pharmacological treatment. This guide brings clarity, actionable insights, and expert advice, so you can finally pinpoint what’s going on inside your head and take the right next steps for your health and comfort.
Ever Wondered If Your Headache Is Really a Migraine or Just Tension? Understanding Migraine Headache vs Tension Headache Location Differences
Many people in the United States and around the world experience frequent head pain, but how do you really know if it's a migraine headache or a tension headache? The distinction between migraine headache vs tension headache location differences is not just academic; knowing the specifics helps guide proper treatment and prevention.
Typical migraines produce a pulsing or throbbing head pain, often unilateral, and are frequently accompanied by sensitivity to light and sound, nausea, or aura. Meanwhile, tension headaches often manifest as a tight band circling the head, causing steady, dull pressure on both sides—a hallmark symptom of tension headaches.
Distinguishing between these two common types of headache disorders isn’t easy, as many symptoms overlap, but focusing on head pain location can aid diagnosis. However, the location and quality of the pain serve as valuable clinical clues. While migraine sufferers tend to pinpoint the pain behind an eye or temple, those with tension headaches describe a widespread ache across the forehead or a squeezing sensation around the head. Using these location cues, along with recognizing migraine triggers and tension headache causes, you can better manage or even prevent your next migraine attack or tension headache episode.

Clarity Begins with Location: Key Migraine Headache vs Tension Headache Location Differences
One of the defining differences between migraines and tension headaches lies in the location of head pain. For most migraines, the ache is unilateral —meaning it appears on only one side of the head, often behind the eye or at the temple. Migraines can shift sides, but they rarely affect the entire head at once.
On the other hand, tension headaches are bilateral and present as a dull, steady pain spanning across the forehead, temples, or wrapping around the entire head like a tight band. This location clue is often the quickest way to tell which type of headache you are experiencing. Differentiating the type headache by location can inform both at-home remedies and decisions about professional care.
For those seeking a deeper dive into the latest therapies, it's helpful to explore the full range of migraine treatment options available today , including both traditional and emerging approaches that can be tailored to your specific headache type and symptoms.
What You'll Discover in This Guide
The anatomy of migraine vs tension headache location differences
How to distinguish between head pain symptoms
Common migraine triggers and tension headache causes
Pharmacological treatments and prevention strategies for both types
Expert opinions on headache management
Defining the Type Headache: Migraine Headache vs Tension Headache
Understanding the characteristics of different types of headaches is essential for accurate self-diagnosis and proper treatment. Migraines and tension headaches, for example, are the most common type of headache disorder seen by health care professionals. Migraines are episodic in nature; each episode is called a migraine attack and features a cluster of symptoms beyond pain, such as nausea and aura.
Tension headaches, on the other hand, are the most common type of headache worldwide. They are characterized primarily by bilateral, non-throbbing pain, with fewer associated symptoms. Understanding the tension headache and migraine patterns can help in proper identification and subsequent management of these conditions.
Overview of Migraine Headache: Anatomy, Patterns, and Location
Migraine headaches are a neurological disorder marked by debilitating, often one-sided throbbing pain. Anatomically, migraines involve changes in neurotransmitter activity, blood vessel dilation, and abnormal signaling within the brain’s pain pathways. This disruption typically results in a pulsing or pounding sensation, with migraine pain centered behind one eye, at the temple, or even radiating to the jaw and neck. Migraines often begin with an "aura"—visual disturbances or sensory changes—before the main attack phase starts.
The location differences help distinguish migraines from other types of headaches. The pain commonly alternates sides from one migraine attack to another, or even during a single episode. Because of the neurological basis, migraine symptoms often go beyond head pain to include sensitivity to light and sound , nausea, vomiting, and dizziness—all crucial clues in the diagnostic process.
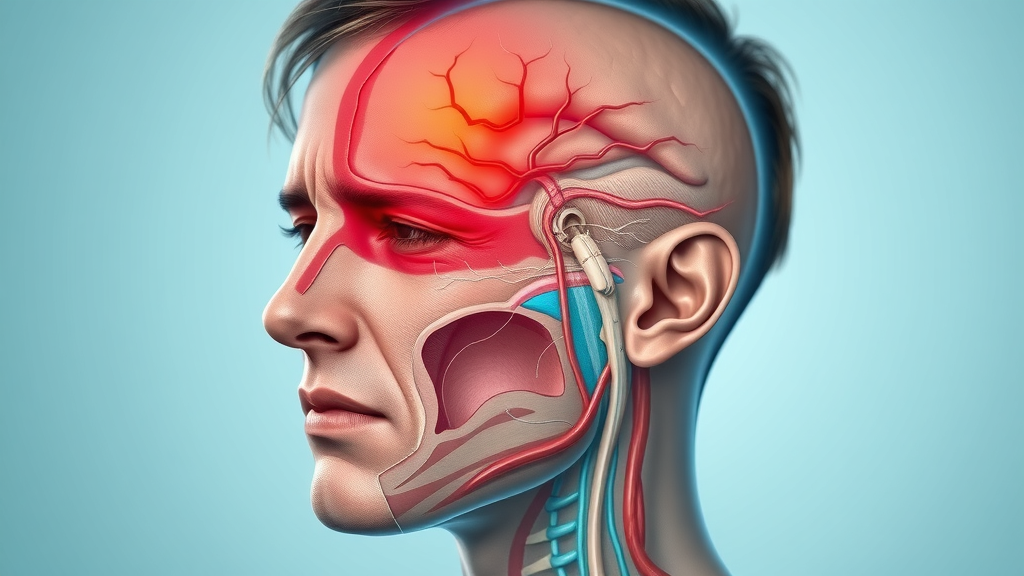
Exploring Tension Headaches: Causes and Head Pain Pathways
Tension headaches produce a very different clinical picture from migraines. Their pain mechanisms are less about vascular changes and more related to muscle tension, poor posture, or stress. The classic feature is pain that is generally bilateral and described as constant pressure or a tight band encircling the head. The pain can also spread to the neck and shoulders—clear signals that muscle tension plays a significant role.
Unlike migraines, tension headaches seldom include nausea or significant sensitivity to light and sound. Instead, sufferers notice a gradual onset of mild to moderate discomfort that can persist for hours or even days, making them challenging to distinguish from other types of headaches without careful tracking of symptoms and triggers. Identifying these criteria is essential to understanding whether you experience a tension headache versus a migraine attack.
Table: Comparison of Migraine Headache vs Tension Headache Location Differences
Feature |
Migraine Headache |
Tension Headache |
|---|---|---|
Typical location |
One side, temple, behind eye |
Forehead, both sides, band-like |
Pain quality |
Throbbing, pulsating |
Dull, pressure, tightening |
Duration |
4-72 hours |
30 min to days |
Associated symptoms |
Nausea, photophobia, aura |
Mild photophobia, rare nausea |
Triggers |
Food, stress, hormonal, sensory |
Stress, poor posture, fatigue |
Spotting the Head Pain: Where Do These Headaches Hurt?
When grappling with head pain , pinpointing the exact pain region is vital for recognizing the distinction between a migraine headache and a tension headache. Migraine headaches most often present with pain on one side of the head, which can be severe and throbbing, sometimes radiating from behind an eye or temple to the side of the face or neck. The location and quality of this pain are distinctive and serve as one of the best diagnostic differentiators.
In contrast, tension headaches tend to blanket the whole head with a constant, dull ache or vice-like pressure. The sensation can wrap around the scalp and is commonly described as "band-like," frequently accompanied by muscle stiffness in the neck and shoulders. Recognizing these location differences can help you identify the correct treatment path and avoid unnecessary discomfort.
Migraine Headache Location Differences and Unique Symptoms
Most migraine headaches start with pain centered behind one eye, at the temple, or on just one side of the head—a hallmark of the condition. This pain is usually pulsating or throbbing and is often aggravated by physical activity. Other symptoms that typically accompany migraines include sensitivity to light and sound , nausea, and sometimes visual aura.
These distinct features are reinforced by the neurological process behind migraines: dilation and inflammation of blood vessels and irritated pain pathways in the brain. Migraines may shift sides or, less frequently, become bilateral, but the "one-sided" presentation remains the gold standard in clinical diagnosis. Recognizing this can speed up effective pharmacological treatment and prompt relief.
Tension Headache Location Differences and Associated Head Pain
Tension headaches tend to cause a diffuse, dull pain that affects both sides of the head. Many sufferers describe it as "pressure" or "tightness" that wraps from the forehead around the back of the head to the neck. Tension headache pain is generally steady, non-pulsating, and less likely to prevent daily activities than a migraine. Occasionally, it’s mistaken for a sinus headache due to the forehead distribution.
The pain does not usually intensify with movement, and rarely includes the additional neurological symptoms that define migraines. Understanding these differences is important to ensure you are not over-treating a tension headache as a migraine headache , thereby avoiding unnecessary medications and related side effects.

Looking at head pain diagrams or animated pain maps can visually clarify where migraines versus tension headaches most commonly strike. In a migraine head pain map, you’ll notice highlighted regions around one temple, behind an eye, or sometimes down the side of the neck—corresponding to classic migraine zones. A tension headache map, however, shades both sides of the head and wraps a band around the forehead and occiput, showcasing the broad distribution typical of this type of headache. Viewing these guides can help users visually connect their own symptoms and localize their pain more effectively.
Clinical Clues: How to Differentiate Tension Headache and Migraine
Clinicians rely on both history and physical examination to differentiate a migraine headache from a tension headache. The location of the pain, presence or absence of neurological symptoms, and a review of symptom patterns over time all provide critical clinical clues. It’s important for patients to note frequency, severity, and triggers—details that help physicians make a precise diagnosis and recommend the best pharmacological treatments.
Migraines are much more likely to present with unilateral, throbbing pain plus additional symptoms (nausea, photophobia, and aura), while tension headaches usually cause a generalized, mild-to-moderate ache with minimal associated features. Keeping a headache diary can help document these patterns and support both self-assessment and professional evaluations.
Differentiating Migraine Headache vs Tension Headache Based on Symptom Location
The most reliable way to distinguish between a migraine headache and a tension headache is by closely evaluating the location and nature of the pain. Migraines characteristically cause throbbing pain on one side of the head, commonly near the eye or at the temple, and frequently come with other symptoms like light sensitivity, visual changes, and nausea.
In contrast, tension headaches generally cause pain on both sides of the head or across the forehead. This pain is often described as steady, tight, or pressurized, lacking the pulsating quality of a migraine. These localization clues, when recognized early, can help guide both self-care and clinical decisions, optimizing pharmacological treatment when necessary.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Consider Anna, a university student who noticed a pounding pain behind her right eye anytime she skipped a meal or experienced high stress. She often felt queasy and sensitive to light—classic indicators of migraine. Meanwhile, John, a software engineer, complained of a tight, pressure-like pain circling his head during long workdays spent hunched over his desk. He never felt sick to his stomach and was able to work through his discomfort—clear signs of tension headaches.
These real-world examples highlight the value of recognizing migraine headache vs tension headache location differences. Accurate self-reporting to a health care provider ensures that appropriate remedies and prevention strategies—be they medications or lifestyle changes—can be prescribed quickly and effectively.

Expert Quote: Neurologists on Location Differences
“While there is some symptom overlap, the most important clinical clue often lies in where and how the pain presents. Migraines are typically one-sided and throbbing, often accompanied by nausea or aura, while tension headaches cause a milder, steady pain that feels like a band wrapping around the head. Recognizing these patterns is essential for fast, effective management.”
– Dr. J. Chen, Board-Certified Neurologist
Chronic Migraine and Its Overlapping Symptoms
Some individuals experience chronic migraine , defined as having headache symptoms on 15 or more days a month, with at least eight days featuring migraine features. Chronic migraine can mimic tension headache in frequency and distribution, making the diagnosis more challenging. Overlap in symptoms, such as widespread pain and reduced severity, can further blur the distinction.
Yet, awareness of migraine headache vs tension headache location differences remains crucial. Frequent, recurring headaches that feature both typical migraine symptoms and tension qualities may require combined therapeutic approaches, regular monitoring, and lifestyle shifts for optimal management and relief.
Chronic Migraine vs Tension Headache: Frequent and Persistent Head Pain
Chronic migraine sufferers often report persistent unilateral pain that alternates sides or becomes more diffuse over time. These headaches can last days and frequently interfere with social, educational, and occupational functioning. By comparison, chronic tension headaches typically result in constant, mild-to-moderate bilateral pain that develops with prolonged stress or poor posture.
This overlap can make diagnosis difficult, necessitating thorough symptom journals that track both the frequency and severity of the pain. Health care providers recommend regular check-ins to differentiate between persistent migraines and chronic tension-type headaches, as the management strategies can diverge significantly.
Identifying Chronic Migraine Triggers: Beyond Just Location
Chronic migraine is influenced by a range of external and internal factors, known as migraine triggers. These can include disrupted sleep, certain foods, hormonal fluctuations, and environmental changes. While location helps identify the type of headache, tracking triggers deepens the understanding and guides long-term management.
For those grappling with chronic head pain, mapping specific triggers—alongside pain locations—enables more accurate interventions, whether pharmacological or lifestyle in nature. Overlooking these triggers can prolong suffering or contribute to headache transformation from episodic to chronic forms.
Personal Story: Living with Chronic Migraine and Recognizing Location Differences
Maria, a graphic designer, experienced severe, pulsating pain behind her left eye so often that she began associating her work deadlines with the onset of a migraine headache. After consulting a specialist and starting a symptom and trigger diary, she recognized a pattern and was able to proactively treat her migraines at the earliest sign. Maria’s story illustrates the power of understanding migraine headache vs tension headache location differences in breaking the cycle of chronic pain and regaining control over daily life.
Migraine Triggers vs Tension Headache Causes
Knowing what ignites your headaches, including common migraine triggers and tension headache causes, is as important as understanding where the head pain occurs. Migraine triggers and tension headache causes often overlap but have unique features that make specific prevention strategies possible. For example, migraines might be spurred by specific foods or hormonal changes, while tension headaches most commonly arise from stress, fatigue, and musculoskeletal strain.
Documenting both the location and trigger profile of your headaches gives a fuller picture, enhancing your self-assessment accuracy and treatment options. An individualized list of triggers can be developed with the help of a headache society specialist or your primary health care provider.
Common Migraine Triggers that Influence Location of Pain
The location of migraine headaches —often behind one eye or at the temple—can sometimes be linked to the trigger itself. For example, exposure to bright light or lack of sleep tends to activate pain pathways on one side of the head, intensifying the classic migraine zones. Other migraine triggers include certain foods (like chocolate or processed meats), hormonal fluctuations, weather changes, and even strong odors.
Understanding your unique migraine triggers, alongside the location of your pain, empowers you to adjust lifestyle factors, identify patterns, and implement avoidance or rapid-response strategies for better control of migraine attacks.

Tension Headaches: Environmental and Emotional Triggers
Tension headaches typically arise from a mix of emotional, psychological, and physical factors. Stress is the most common type of trigger, but poor posture, dehydration, and long hours staring at screens also contribute. These headaches often start with tension in the neck or scalp, gradually developing into a dull, bilateral ache spanning the entire head.
By consciously monitoring these contributing factors and implementing regular breaks or relaxation methods, many tension headache sufferers can minimize frequency and severity—no prescription needed.
Checklist: Self-Assessment for Headache Causes
Does your pain start on one side (migraine) or both sides (tension)?
Is the pain pulsating and severe (migraine), or steady and mild-to-moderate (tension)?
Do your headaches occur alongside nausea, visual changes, or light sensitivity (migraine)?
Are stress, posture, or fatigue frequent triggers (tension)?
Does your pain last hours to days, with significant impairment (migraine/chronic)?
Pharmacological Treatment Approaches for Migraine and Tension Headaches
Effective management of migraine headache vs tension headache location differences often involves tailored pharmacological treatments specific to each headache type. The right medication can make all the difference but must be chosen based on accurate diagnosis and symptom patterns. Migraines may respond well to triptans, ergotamines, or preventive pharmacological treatments, whereas tension headaches often improve with NSAIDs, acetaminophen, or muscle relaxants.
Both migraine headaches and tension headaches can benefit from acute rescue medications, but only chronic migraine requires long-term pharmacological treatment. Combining medication with lifestyle management and routine follow ups with health care providers forms the gold standard for achieving long-term relief.
Pharmacological Treatments: Options for Chronic Migraine and Head Pain
For chronic migraine sufferers, pharmacological treatment may require a multi-pronged approach, using both daily preventive medication and acute relief drugs for breakthrough pain. Preventive medications include beta blockers, certain anticonvulsants, and CGRP inhibitors. For acute attacks, triptans, NSAIDs, or gepants are often prescribed.
Overuse of acute medications, however, can lead to medication-overuse headaches—a complication health care professionals vigilantly monitor. Tailored treatment plans, balancing preventive and rescue medications, offer the best outcomes for chronic or severe headache disorders.
Tension Headache Pharmacological and Lifestyle Management
Tension headache treatment relies mainly on over-the-counter medications, such as ibuprofen, aspirin, or acetaminophen. For persistent or frequent cases, a physician may suggest low-dose antidepressants or muscle relaxants to break the headache cycle. Lifestyle-based interventions are equally important, with focus on routine, adequate hydration, ergonomic work setups, and regular exercise.
Integrating lifestyle management with occasional pharmacological support is an effective and safe long-term strategy for most sufferers of tension headaches, minimizing risks and maximizing daily comfort.
Video Explanation: Medications for Different Headaches
Visual resources, such as video breakdowns presented by headache society neurologists, can assist in understanding which medications are best for your type of headache. Watching a medication guide helps clarify differences in drug classes, dosing, and potential side effects for migraine and tension headaches , ensuring you arrive at your health care appointment well informed and prepared with questions.
Non-Pharmacological Relief: Beyond Medication
Medication isn’t the only answer. A growing body of research highlights the value of non-pharmacological approaches for both migraine and tension headache relief. Lifestyle modifications, stress management, and targeted home remedies can make a tangible difference—sometimes reducing reliance on medications altogether. Mindful practices, stretching, yoga, and cognitive-behavioral techniques are leading the charge in headache prevention and management.
Discussing these options with your health care provider ensures a balanced approach to headache relief and can be tailored to your specific pain patterns and triggers for the greatest success.
Lifestyle Changes for Migraine and Tension Headache Pain
Simple lifestyle changes can lead to dramatic reductions in headache frequency and severity. Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, managing stress through meditation or breathing exercises, regular physical activity, balanced nutrition, and ergonomic workspaces all contribute to minimizing the onset of both migraines and tension headaches.
These strategies are especially effective when paired with awareness of head pain location and triggers—empowering sufferers to take control, one healthy habit at a time.

Effective Home Remedies: Location-Specific Pain Management
Apply a cold pack to the side of the head for migraine relief
Use a warm compress on the neck or shoulders to reduce tension headache pain
Try gentle neck and upper-back stretches to relieve muscle-induced tension
Practice guided relaxation or meditation to ease both migraine and tension symptoms
Keep a detailed headache diary tracking location, triggers, and remedies
Quotes from Headache Sufferers on Successful Strategies
“Recognizing that my headaches started behind my left eye made all the difference. Now, I can treat migraines before they ruin my day.”—Liam S.
“Switching to a standing desk and taking stretch breaks every hour virtually eliminated my tension headaches!”—Kendra W.
When to Seek Medical Advice for Migraine Headache vs Tension Headache Location Differences
Most headaches are harmless, but certain warning signs indicate the need for immediate medical attention. Persistent, severe, or rapidly worsening headaches, new onset after age 50, or those paired with neurological symptoms (weakness, speech changes, confusion) are cause for concern. Always seek professional evaluation if your headaches change in frequency, duration, or character—especially if they disrupt daily life or fail to respond to usual remedies.
Preparation increases the value of your neurology appointment. Keep records of headache frequency, precise locations, associated symptoms, and attempted remedies for a more targeted and accurate assessment.
Warning Signs and Red Flags: Differentiating Head Pain
Sudden, thunderclap headache (worst headache of your life)
Headache accompanied by fever, stiff neck, vision changes, or loss of consciousness
Progressive headache, worsening every day
Headaches following head trauma
Neurological symptoms: weakness, numbness, difficulty speaking, confusion
Preparing for Your Neurologist Visit: What Information Is Crucial?
Headache onset, location, and frequency
Characteristics (throbbing vs pressure, one side vs both sides)
Associated symptoms (nausea, aura, visual changes)
Any known triggers or patterns
Previous treatments and their effectiveness
People Also Ask: How to Differentiate Tension Headache and Migraine?
Understanding the Defining Factors
Differentiating between tension headaches and migraines comes down to analyzing the pain’s quality, location, and associated symptoms. Tension headaches present as a dull, steady ache on both sides of the head, feeling like a band, with minimal additional symptoms. Migraines, on the other hand, lead to pulsating, intense pain on one side with possible nausea, light/sound sensitivity, and aura.
Learn how to tell a tension headache from a migraine by evaluating location, severity, associated symptoms, and response to typical triggers. Tension headaches often cause a dull, pressurized pain across the forehead or around the head, while migraines are more likely to cause throbbing, unilateral pain, sometimes with nausea, light/sound sensitivity, or visual disturbances.
By evaluating your pain's position, nature, and triggers, you can reliably determine whether your headache is more likely a tension-type or a migraine. Seek the advice of a health care professional if you’re unsure, or if the pain is severe and persistent.
People Also Ask: What Type of Headache Do I Have Based on Location?
Mapping Your Pain
Location plays a key role in identifying your type of headache. If your pain is a tight band encircling your head or a general pressure across both sides, you’re likely dealing with a tension headache. If your pain is focused around the temple, behind one eye, or on only one side of your head, especially if it’s throbbing or pulsing, it’s most likely a migraine.
Analyze whether the pain is bilateral and band-like (tension) or unilateral and pulsating (migraine), using headache location as a reliable indicator to help you identify the type of headache you may be experiencing.
Detailed self-mapping and symptom tracking can support more informed discussions with your doctor and quicker resolve to your discomfort.
People Also Ask: Which Part of Your Head Hurts During a Migraine?
Unilateral vs Bilateral Pain
Migraines most often cause unilateral head pain —meaning pain is felt on just one side, usually behind the eye, above the temple, or sweeping into the neck and face. However, some migraine attacks can shift sides or, less commonly, encompass both sides during the same episode.
Migraines commonly affect one side of the head, particularly behind the eye or temple, but can also radiate to the entire side or shift sides from attack to attack.
This one-sided pain is a major clue in identifying a migraine headache rather than a tension headache.
People Also Ask: How Do I Know If My Headache Is from Tension?
Typical Tension Headache Symptoms
Tension headaches present with a constant, dull ache or sensation of tightness on both sides of the head. Many compare it to a “vice grip” or a band compressing the skull. Tension headaches are less intense than migraines and typically do not interfere with daily activities to the same degree.
Tension headaches usually present as a constant, dull ache or pressure on both sides of the head, often described as a tight band. They are less likely to cause nausea, aura, or heightened sensitivity to light and sound.
If your headaches feature these characteristics, you are probably dealing with a tension-type headache rather than a migraine.

FAQs: Migraine Headache vs Tension Headache Location Differences
Can tension headaches turn into migraines?
While rare, tension headaches can sometimes transition into migraines if triggers overlap or untreated tension leads to escalating neural changes. However, most cases remain distinct types—knowing your headache's characteristics and triggers is crucial for preventing escalation.
What lifestyle changes can help reduce both types of headaches?
Consistent sleep, hydration, stress management (meditation, yoga), regular exercise, and ergonomic improvements to your work environment are key. These lifestyle shifts address both the physical and emotional factors behind migraines and tension headaches, often reducing frequency and severity significantly.
Are treatments for migraine headache vs tension headache location differences ever combined?
Yes, in cases of overlapping or chronic symptoms, doctors sometimes use a combination of medications (preventive plus acute) and lifestyle measures. Knowing your pain location and trigger patterns helps your health care provider tailor a comprehensive plan just for you.
What are common misconceptions about headache locations?
Many believe migraines always affect one side or that all severe pain is a migraine. In truth, migraine attacks can occasionally present bilaterally, and tension headaches can occasionally be intense. Assess all symptoms and consult a specialist if you’re unsure.
Headache Location Quick Reference Table
Feature |
Migraine Headache |
Tension Headache |
|---|---|---|
Typical location |
One side, temple, behind eye |
Forehead, both sides, band-like |
Pain quality |
Throbbing, pulsating |
Dull, pressure, tightening |
Duration |
4-72 hours |
30 min to days |
Associated symptoms |
Nausea, photophobia, aura |
Mild photophobia, rare nausea |
Triggers |
Food, stress, hormonal, sensory |
Stress, poor posture, fatigue |
Summary and Final Insights on Migraine Headache vs Tension Headache Location Differences
Take the Next Step Toward Understanding Your Head Pain
Empower yourself by recognizing migraine headache vs tension headache location differences and seek personalized care for optimal relief.
If you’re ready to take your understanding of headache management even further, consider how your symptoms might impact other areas of life, such as work or daily functioning. For those navigating frequent or severe migraines, learning about the connection between migraines and disability benefits can provide valuable perspective and practical next steps. Exploring these broader implications ensures you’re not only managing pain, but also advocating for your overall well-being and long-term quality of life.
Watch this comprehensive Q&A video featuring expert neurologists as they answer common questions, discuss case examples, and share new perspectives on managing migraine and tension headaches based on their locations and symptoms.
Understanding the differences between migraine and tension headaches is crucial for effective management and treatment. Migraines typically present as throbbing or pulsating pain, often on one side of the head, and may be accompanied by nausea, sensitivity to light and sound, and visual disturbances. In contrast, tension headaches usually cause a dull, aching pain on both sides of the head, often described as a sensation of tightness or pressure around the forehead or back of the head. ( medicalnewstoday.com )
For a comprehensive comparison of these headache types, including their symptoms, causes, and treatments, you may find the article “Migraine vs. tension headache” helpful. ( medicalnewstoday.com )
Additionally, the article “Tension Headache vs. Migraine: Differences, Symptoms, and Treatments” provides detailed insights into distinguishing features and management strategies for both conditions. ( webmd.com )
If you’re serious about understanding and managing your headaches, these resources will provide valuable information to help you identify your symptoms and seek appropriate care.
Disclaimer: The information provided on this website is for general informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a qualified healthcare professional before making any decisions or taking actions related to your health, including but not limited to medical conditions, devices, treatments, diets, supplements, or exercise programs. The content on this site is not intended to replace professional medical guidance. The website and its authors are not responsible for any actions taken based on the information provided. Ask your doctor or licensed medical professional first.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




Write A Comment