Permanent birth control sounds simple — one quick procedure and you’re done. But tubal ligation has hidden pros, cons, and long-term effects every woman deserves to understand before deciding. If you're thinking about getting your tubes tied, there’s a lot more beneath the surface than most people—or even some doctors—will tell you.
A Surprising Perspective on the Pros and Cons of Tubal Ligation
Clear definition of tubal ligation and how the procedure works
Unfiltered facts: pros and cons of tubal ligation, including long-term implications
Expert insights and real-life examples for those considering having their tubes tied
Comparison of tubal ligation to other birth control methods
Detailed explanation of recovery time, side effects, and potential negative effects
Answers to frequently asked questions about tubal ligation
"Almost 1 in 4 women in the U.S. choose permanent birth control, yet most wish they’d known more about the hidden challenges—and benefits—of tubal ligation." – Dr. Alexis Carter, OB/GYN

What Is Tubal Ligation? Understanding the Procedure and the Main Pros and Cons
A Quick Overview: Tubal Ligation (Tubes Tied) as a Birth Control Method
Tubal ligation, commonly known as getting your tubes tied, is a permanent form of birth control chosen by millions of women in the U.S. and around the world. The procedure involves surgically blocking or cutting the fallopian tubes, preventing eggs from traveling to the uterus where fertilization can occur. Many opt for tubal ligation when their family is complete or when they seek a long-term, highly effective solution. Unlike daily or monthly birth control options, this control method offers convenience and peace of mind. However, the decision isn’t simple—there are important pros and cons that most women don’t hear until after the fact. Understanding both the benefits and the potential drawbacks puts you in the driver’s seat, so you’re empowered to make the right call for your body and your future.
While tubal ligation is praised for its effectiveness in preventing pregnancy—more than 99%—it’s not a decision to take lightly. Recovery time, potential side effects, and the irreversibility of the procedure deserve honest discussion. With expert insights, this guide unpacks what it really means to have your tubes tied so you can approach this permanent birth control method with confidence.
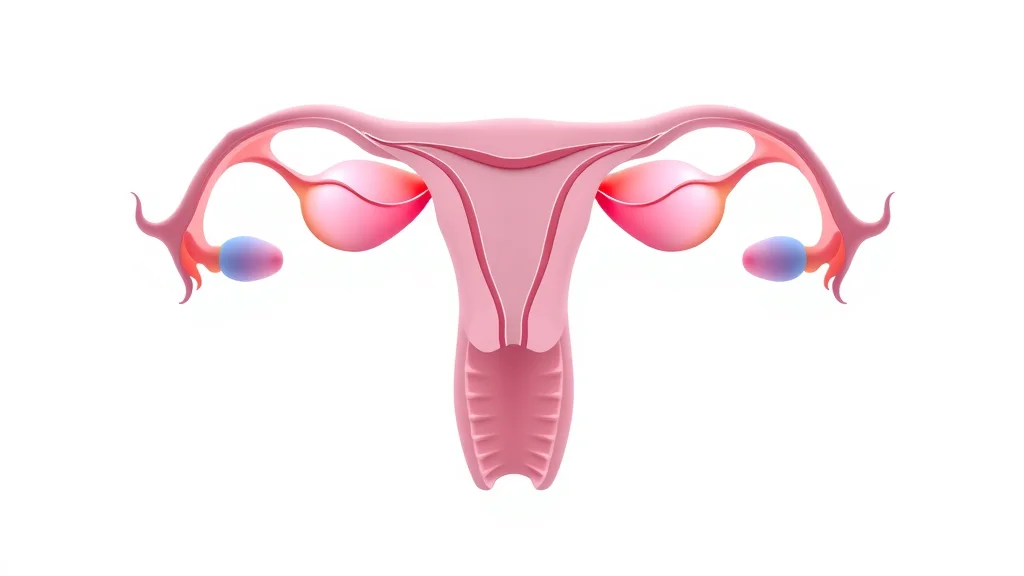
How Does Tubal Ligation Surgery Work? Exploring Laparoscopic Tubal Ligation
Most modern tubal ligations are performed using minimally invasive laparoscopic techniques. During a laparoscopic tubal ligation, a surgeon makes a small incision near the belly button and inserts special instruments and a camera. The fallopian tubes are then located, clipped, sealed, or cut and tied—a process that takes about 30–60 minutes and is typically an outpatient procedure. Since only a small incision is made, most women go home the same day and return to light activities in a few days.
Laparoscopic tubal ligation offers several advantages compared to more invasive surgical procedures, including reduced recovery time, lower risk of infection, and limited scarring. However, like any surgery, there are side effects and surgical risks, such as reaction to anesthesia or post-surgery discomfort. It’s important to discuss how this ligation surgery works with your care provider and to ask questions about your own medical history, especially if you have underlying health conditions, to decide if this form of birth control is right for you.
As you weigh the pros and cons of tubal ligation, it’s also helpful to consider how your overall wellness and recovery can be supported. For instance, focusing on nutrition and lifestyle can play a role in healing and long-term health. If you’re interested in practical ways to boost your body’s strength and resilience, explore these evidence-based foods that help strengthen your legs and support overall wellness.
Fallopian Tubes & Female Anatomy: The Science Behind Tubal Ligation
The fallopian tubes play a pivotal role in reproduction, acting as passageways for eggs to travel from the ovaries to the uterus. Tubal ligation works by disrupting this pathway. When the tubes are cut, blocked, or sealed, sperm cannot meet the egg, effectively preventing pregnancy. The rest of the reproductive system, including hormonal balance and egg production, remains unaffected since the ovaries and uterus stay untouched by the procedure.
However, understanding the anatomy helps clarify certain risks—such as the rare but serious occurrence of ectopic pregnancy, where a fertilized egg implants in the fallopian tube. Knowing the basics of female anatomy and how tubal ligation fits into the larger picture of birth control empowers you to understand both the benefits and possible complications of this permanent procedure.
Comparing Permanent Birth Control Methods: Tubal Ligation vs. Other Options
Control Method |
Effectiveness |
Maintenance |
Reversibility |
Hormones |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Tubal Ligation (Tubes Tied) |
99%+ |
None (once done) |
Generally permanent |
Non-hormonal |
Vasectomy (Male) |
99%+ |
None (once done) |
Difficult to reverse |
Non-hormonal |
Intrauterine Device (IUD) |
97–99% |
5–10 years per device |
Yes, removed easily |
Hormonal/Non-hormonal |
Birth Control Pills |
91–99% |
Daily |
Yes |
Hormonal |
Implants |
99%+ |
3–5 years per implant |
Yes, removed easily |
Hormonal |
The Pros of Tubal Ligation: Why Some Women Choose to Have Their Tubes Tied
Permanent, Highly Effective Birth Control (Birth Control Method Security)
No daily or monthly maintenance
No hormones or ongoing prescriptions
Decades-long effectiveness
Perhaps the main reason women choose tubal ligation is the unmatched peace of mind it brings. As a birth control method, it’s essentially set-and-forget: there are no pills to remember, patches to change, or prescriptions to fill. For women who know their family is complete or who cannot use hormonal forms of birth control due to medical reasons, the permanence of tubal ligation is both a relief and a huge convenience. In addition, the decades-long track record of effectiveness is compelling—statistics show that less than 1% of women experience an unexpected pregnancy after the procedure.
Unlike temporary options such as IUDs or implants—which require periodic replacements—or birth control pills that must be taken consistently, tubal ligation eliminates nearly all the ongoing work associated with birth control. For many, this alone justifies the decision and outweighs the risks or downsides.

Confidence and Peace of Mind: The Psychological Benefits
Aside from its medical advantages, tubal ligation offers significant psychological benefits. Many women report a new sense of freedom and autonomy—no more racing thoughts about missed pills or pregnancy scares. This peace of mind can improve relationships and support a less stressful sex life, which is often underappreciated in traditional discussions around birth control. The decision to get your tubes tied can feel empowering, especially for women with busy lives, irregular schedules, or underlying medical conditions that make other birth control methods unsuitable.
It’s not only about pregnancy prevention, but also the confidence that comes from making a proactive, intentional decision about your reproductive health. Over time, this can lead to a more relaxed and balanced emotional life—an essential “pro” that can be life-changing for certain individuals.
Non-Hormonal: How Tubal Ligation Differs from Hormonal Birth Control
Tubal ligation provides non-hormonal birth control. This is crucial for women who experience unwanted side effects from hormonal methods like the pill, patch, or IUD—including mood swings, weight changes, or migraines. As a surgical solution, tubal ligation alters only the fallopian tube pathway; it doesn’t affect the ovaries’ hormone production or menstrual cycle regulation for most women.
The non-hormonal aspect means your body’s natural rhythms can proceed unimpeded. Many women appreciate this difference, especially if they’ve struggled with the side effects of other forms of birth control. If your goal is to avoid hormones altogether, tubal ligation stands out as a highly effective option.
"For women who know their family is complete, tubal ligation offers unmatched simplicity and certainty."
The Cons of Tubal Ligation: What They Don’t Often Tell You
Surgical Risks and Side Effects: What Are the Potential Dangers of Tubal Ligation Surgery?
Anesthesia risks and complications
Short-term post-surgical pain
Possible long-term side effects
No surgery is without risks—even a minimally invasive laparoscopic tubal ligation. During the procedure, you’ll be under anesthesia, which brings its own set of complications, although these are rare. Post-surgical pain around the incision (often by the belly button) and the internal sites where the tubes are blocked or cut is common for a few days. Most women find discomfort manageable, but bruising and fatigue may last up to a week.
“Tubal ligation is a permanent contraception method, usually done laparoscopically with rapid recovery and high effectiveness, but it’s important for patients to fully understand the pros and cons before deciding.” - Dr. Erica Schipper, Sanford Health
Very rarely, more serious complications can occur—such as infection, bleeding, or adverse reactions to anesthesia. Long-term, some women report persistent pain or changes in their menstrual cycle. Healthcare providers recommend carefully weighing these potential side effects and discussing your entire medical history before choosing this procedure. No control method is without drawbacks, but being fully informed helps avoid surprises post-surgery.

Irreversibility: Can Tubal Ligation Be Undone?
This might be the most important “con” of all: tubal ligation is considered a permanent procedure. While reversal surgeries exist, they are costly, involve more invasive operations, and are not always successful—especially if your tubes were removed or extensively damaged in the initial procedure. Many women who opt for reversal don’t achieve pregnancy, making it crucial to be 100% certain about not wanting future children. This permanence can lead to regret if life circumstances or desires change later, and is a key reason for thoroughly consulting with a care provider before deciding on this option.
Some providers may recommend counseling or a waiting period to ensure you are fully confident about moving forward. It’s also a good idea to explore all other forms of birth control, especially if there is any possibility you’ll want to grow your family in the future.
Possible Changes to Menstrual Cycle and Hormonal Balance
Tubal ligation is not supposed to affect hormonal function, but some women notice changes in their menstrual cycle after the procedure. This might include heavier, lighter, or irregular periods in the months following surgery. The medical community is divided on whether tubal ligation directly causes these changes, or if other factors like coming off hormonal birth control or aging are to blame. However, these possibilities are worth noting. Some women, especially those with a history of difficult periods, might see their symptoms persist or worsen.
If you rely on hormones in your birth control to regulate your cycle, bear in mind that tubal ligation doesn’t offer this benefit. It’s primarily designed for pregnancy prevention and not for symptom management of conditions like endometriosis or heavy bleeding. Talk candidly with your provider about what changes to expect, so you’re not caught off guard post-surgery.
“Tubal ligation is recommended for adult women who have had time to weigh the benefits against the potential disadvantages and risks carefully… Given the complexity and uncertainty of reversal surgery, doctors recommend that women not rush into the decision to have their tubes tied and only move forward once they are confident that permanent sterilization is the right choice.” - Dr. Lodge, Cool Springs OB-GYN
Emotional or Psychological Impact After Tubes Tied
The emotional journey doesn’t end with the surgery. While many women report feeling empowered, others experience regret, sadness, or even loss—especially if they undergo tubal ligation at a younger age or under pressure. These emotional effects may be tied to changing life circumstances, new relationships, or unanticipated feelings of finality. It’s important to weigh not only the physical but also the psychological side effects, and to discuss these openly with your care provider and support network.
Even if the initial motivation is clear, real-life stories show that people’s perspectives can shift, making mental preparation just as important as understanding the procedural risks. Support groups or therapy may help in processing complex feelings after getting your tubes tied.

Rare Complications: Risk of Ectopic Pregnancy and Fallopian Tube Issues
One of the rare but serious risks of tubal ligation is ectopic pregnancy, where a fertilized egg implants in a remaining section of the fallopian tube. Although very uncommon, an ectopic pregnancy can be life-threatening and requires emergency medical intervention. In addition, scar tissue (adhesions) can occasionally cause chronic pain or complications involving surrounding organs.
Understanding these rare risks is critical—ask your provider about your individual risk profile and understand the symptoms of possible complications so you can act quickly if needed. Although the majority of women never experience these issues, it’s wise to be prepared and proactive about your reproductive health long after the procedure is finished.
Recovery Time After Tubal Ligation: What to Expect and How to Prepare
How Long Is Recovery After Tubal Ligation?
The recovery time following a tubal ligation is generally short, especially with a laparoscopic or minimally invasive approach. Most women are up and walking the same day, and full recovery typically occurs within a week. However, some may need up to two weeks to feel fully back to normal, especially if they have a physically demanding job or develop mild complications like infection or prolonged pain near the incision or internally. Your personal experience will also depend on your overall health and history with surgical procedures.
In the first 24–48 hours, it’s common to experience abdominal pain, soreness at the surgery site (often by the belly button), gas pain from the laparoscopic technique, and general fatigue. A care provider should outline what’s normal and what’s not, so you’ll know when to seek additional medical guidance during recovery.

Managing Side Effects and Returning to Normal Activities
Typical discomforts and their duration
Support tips for a smooth recovery at home
Short-term side effects—including light vaginal bleeding, mild cramping, bloating, and temporary shoulder pain (from surgical gas)—usually resolve within several days. Your provider may recommend over-the-counter pain relievers, gentle movement, and proper wound care to ease discomfort. Keeping the incision clean and watching for signs of infection (redness, pus, worsening pain) is essential. Avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and sexual intercourse for about a week, unless your provider gives you specific clearance.
Support networks matter. Enlist family or friends to help with meals, childcare, or chores. Most women return to work and daily routines within 3 to 7 days, but every recovery is unique. Prioritizing rest and following medical advice can make the process smoother and get you back to feeling like yourself quickly.
Personal Experiences: Stories from Women After Getting Tubes Tied
Many women are pleasantly surprised at how straightforward recovery can be, with the majority reporting only minor discomforts and a swift return to normalcy. For example, Alexis, a mother of three from Austin, shared that she was back walking her kids to school within a week. On the other hand, Jenna experienced low energy and a sense of loss for several weeks, emphasizing the individual nature of recovery and emotional impact. Real stories like these highlight the importance of preparing for both the physical and psychological aspects of this choice.
Joining online forums or local support groups can be a valuable source of reassurance and first-hand tips for recovery and long-term adjustment.
Comparing Tubal Ligation to Other Birth Control Options

Tubal Ligation vs. Other Permanent Birth Control Methods
Tubal ligation stands out among permanent birth control methods because it is designed specifically for women who want to end their fertility for good. The main alternative is vasectomy for men, which is less invasive and carries fewer surgical risks—but the ultimate decision depends on family dynamics and mutual agreement between partners. Compared to other female sterilization options (like removal of the fallopian tubes), traditional tubal ligation is less invasive and offers a reliable long-term solution, although new evidence shows removing the tubes may also reduce ovarian cancer risk.
When considering other forms of birth control that are long-term but reversible, like intrauterine devices (IUDs) or hormonal implants, the permanent nature of tubal ligation is both its biggest advantage and potential drawback. Always discuss all options with a healthcare provider to find what best matches your goals, health history, and lifestyle needs.
Pros and Cons Compared: Tubal Ligation, IUDs, Pills, and Implants
Table-based comparisons are helpful for seeing the big picture. Tubal ligation offers non-hormonal, permanent pregnancy prevention; IUDs and implants provide long-term but reversible options; while pills offer hormonal flexibility but require daily commitment. Each control method has its own blend of convenience, side effects, and effectiveness that should be assessed for your particular life and health situation.
If you’re sensitive to hormones or want long-lasting fertility control with no maintenance, tubal ligation or certain copper IUDs might appeal to you. If you may want children in the future, reversible options like IUDs or implants are typically better choices. Comparisons like the one below can clarify complex decisions.
Quick Comparison: Pros and Cons of Tubal Ligation vs. Common Control Methods
Method |
Pros |
Cons |
Hormonal? |
Reversible? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Tubal Ligation |
Permanent, no maintenance, non-hormonal |
Surgical risks, not easily reversible, possible regret |
No |
No |
IUD (Hormonal/Copper) |
Highly effective, lasts years, reversible |
Cramping, possible expulsion, requires insertion |
Yes/No |
Yes |
Birth Control Pills |
Flexible, helps with cycle regulation |
Must be taken daily, hormone side effects |
Yes |
Yes |
Implant |
Long-lasting, highly effective |
Requires minor procedure, hormone effects |
Yes |
Yes |
People Also Ask (FAQs on Tubal Ligation)
What are the disadvantages of getting your tubes tied?
Detailed Answer: Drawbacks may include surgical and anesthesia risks, regret over permanence, changes to menstrual cycle, potential surgical complications, and possible impact on emotional health. Long-term satisfaction varies depending on life circumstances and reason for choosing the procedure.
Are there long-term side effects of tubal ligation?
Detailed Answer: While most women experience few long-term side effects, some report heavier periods or pain, and a very small risk of ectopic pregnancy remains. Major hormonal changes are rare.
Why is tubal ligation not recommended?
Detailed Answer: Tubal ligation isn’t recommended for women who might want more children, have health conditions increasing surgical risk, or could benefit from a reversible birth control method. Consulting a healthcare provider ensures the best personal decision.
What are the negative effects of tubal ligation?
Detailed Answer: Negative effects can include surgical complications, regret, potential changes to menstrual cycle, and in rare cases, psychological distress or increased risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Expert Quotes & Insights: What Doctors and Patients Say About Tubal Ligation
"It’s a personal decision—permanent, but for many, freeing. Consider every angle, including your future feelings, before opting for tubal ligation." — Dr. Jennifer Lee, Reproductive Health Specialist
Key Takeaways: Quick Pros and Cons of Tubal Ligation
Tubal ligation is a powerful, permanent birth control option with both clear advantages and under-discussed downsides.
Recovery is typically straightforward, but emotional and physical impacts vary.
Make an informed, personalized choice based on your health, goals, and life stage.

Final Thoughts: Is The Pros and Cons of Tubal Ligation the Right Choice for You?
"Permanent methods like tubal ligation can be life-changing. Always choose with confidence, knowledge, and expert guidance."

Ready to make an informed decision about the pros and cons of tubal ligation? Start a confidential consultation with a qualified healthcare provider today.
If you’re seeking to make empowered choices about your health, it’s worth expanding your perspective beyond just the clinical facts. Modern wellness is about integrating practical wisdom with up-to-date strategies for self-care and prevention. For a fresh take on everyday health habits that go beyond what you might have learned growing up, discover these essential health tips that blend modern science with actionable advice. Exploring these insights can help you build a foundation for lifelong wellness, no matter where you are on your reproductive health journey.
References
When considering tubal ligation, it’s essential to weigh both its advantages and potential drawbacks. The Mayo Clinic provides a comprehensive overview of the procedure, detailing how it works, its effectiveness, and associated risks. (mayoclinic.org)
Additionally, WebMD offers insights into the pros and cons of getting your tubes tied, including its permanence, effectiveness, and impact on hormonal balance. (webmd.com) These resources can help you make an informed decision about whether tubal ligation is the right choice for your reproductive health. NCWellnessHub.com
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




Write A Comment