
Strengthening Focus and Clarity: Two Proven Mindfulness Techniques for Enhanced Attention and Mental Performance
In today's distraction-heavy world, maintaining focus and mental clarity is a significant challenge for many individuals. Research shows that mindfulness practices can be a powerful and effective approach to improving cognitive function, including sustained attention and executive control.
This article explores two evidence-based mindfulness techniques—Focused Attention Meditation and Mental Noting—that are simple to practice yet profoundly effective in building concentration and mental clarity.
Focused Attention Meditation: Training the Mind to Sustain Focus
Definition and Practice
Focused Attention Meditation (FAM) involves directing attention to a single object, such as the breath, a sound, or a visual point, and actively bringing the attention back whenever it drifts. This practice helps develop sustained attention and cognitive control.
Scientific Support
According to a review published in Nature Reviews Neuroscience by Tang, Hölzel, and Posner (2015), Focused Attention Meditation has been linked to enhancements in attentional stability and executive functioning. The researchers explain that through regular practice, individuals develop stronger neural connections in brain regions associated with self-regulation and goal-oriented behavior, particularly in the prefrontal cortex. (Tang, Hölzel & Posner, 2015)
A study conducted by MacLean et al. (2010) further demonstrated that participants undergoing intensive meditation training showed significant improvements in sustained attention and perceptual discrimination abilities. (MacLean et al., 2010, Psychological Science)
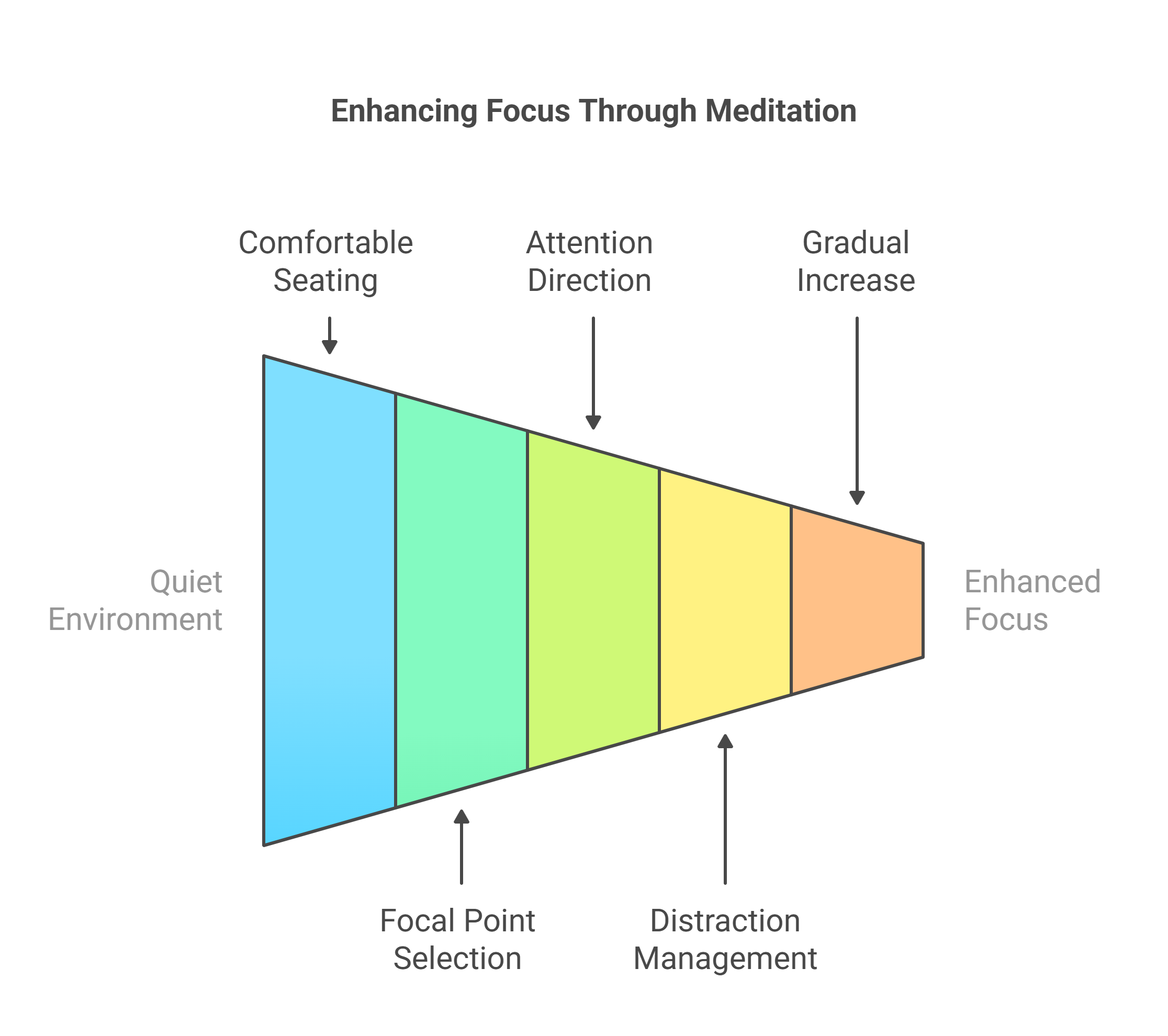
Practical Steps for Focused Attention Meditation:
Find a quiet environment and sit comfortably.
Choose a focal point (e.g., the sensation of breathing).
Direct your full attention to the focal point.
When distractions arise, non-judgmentally acknowledge them and redirect focus back to the original point.
Begin with 5–10 minutes daily, gradually increasing over time.
Mental Noting: Cultivating Meta-Awareness to Clarify Thought Processes
Definition and Practice
Mental Noting is a mindfulness technique in which individuals silently label the nature of experiences as they arise, such as "thinking," "hearing," or "feeling." This method supports meta-cognitive awareness, allowing individuals to recognize and disengage from distracting thoughts without becoming entangled in them.
Scientific Support
Research led by Dr. Judson Brewer, a psychiatrist and neuroscientist at Brown University, has shown that mental noting and similar mindfulness-based interventions help reduce cognitive wandering and emotional reactivity. His work emphasizes how labeling internal experiences can interrupt habitual thought loops, thereby promoting greater mental clarity and emotional regulation. (Brewer et al., 2011, Mindfulness)
Additionally, a study in Consciousness and Cognition by Lutz et al. (2008) indicated that mindfulness practices involving meta-awareness techniques lead to improvements in sustained attention, decreased distractibility, and increased cognitive flexibility. (Lutz, Slagter, Dunne, & Davidson, 2008)
Practical Steps for Mental Noting:
Sit quietly and allow experiences (thoughts, emotions, sensations) to arise naturally.
Gently apply a mental label to each experience as it occurs (e.g., "thinking," "hearing," "planning").
After labeling, return to the original object of focus or simply observe the flow of experiences with clarity.
Practice for short intervals, gradually increasing as comfort with the technique develops.
The Broader Benefits of Mindfulness for Cognitive Health
The benefits of mindfulness practices extend beyond improved attention and clarity. According to a comprehensive meta-analysis published in Clinical Psychology Review, mindfulness training has been associated with enhanced emotional regulation, reduced psychological distress, and better overall cognitive performance. (Khoury et al., 2013)
Furthermore, the American Psychological Association (APA) recognizes mindfulness as an evidence-based intervention for improving not only mental health but also workplace productivity and academic performance, highlighting its applicability across diverse sectors.
Conclusion
Developing focus and mental clarity is an achievable goal through consistent mindfulness practice. Techniques such as Focused Attention Meditation and Mental Noting are supported by a growing body of scientific research and offer structured, accessible methods for enhancing cognitive function.
By integrating these practices into daily life, individuals can cultivate stronger attention, clearer thinking, and greater resilience in the face of everyday distractions.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 

Write A Comment