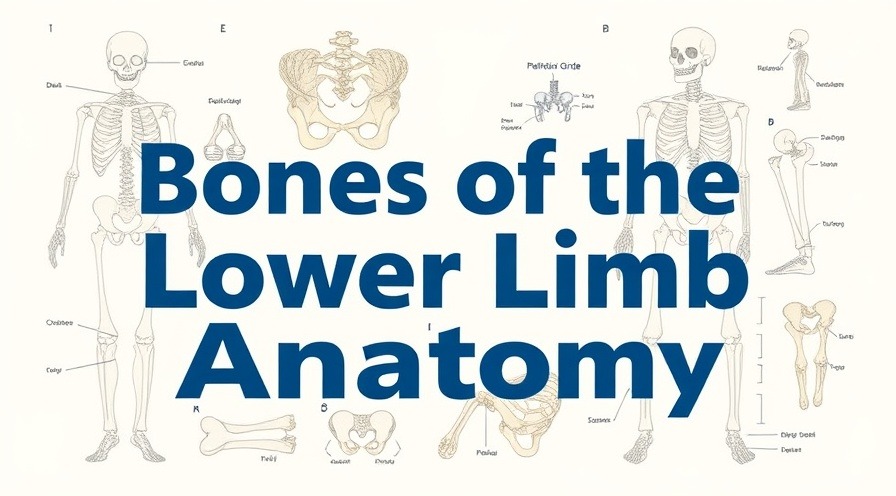
The Fascinating Skeleton of the Lower Limbs: A Detailed Overview
The human skeletal system is a marvel of engineering, and understanding it can provide tremendous insights into our health and wellness, particularly for health-conscious individuals. Among the most intricate parts of this system is the lower limb, which plays a crucial role in our mobility and overall physical health. Let's explore the fascinating skeleton of the lower limbs, focusing on their anatomical structure and functionality, drawing from the educational video, Bones of the Lower Limb: Anatomy.
In Bones of the Lower Limb: Anatomy, the discussion dives into the complex intricacies of our skeletal structure below the waist, exploring key insights that sparked deeper analysis on our end.
Pelvic Girdle: The Foundation of Your Lower Limbs
The pelvic girdle is not just a set of bones; it’s a complex structure that connects the lower limbs to the axial skeleton. This bony ring includes the right and left hipbones and the sacrum. Each hipbone has distinct sections: the illium, ischium, and pubis. The illium, the largest part, is essential for muscle attachment, supporting numerous functions from balance to running. The ischium contributes to your ability to sit comfortably, while the pubis aids in forming the pelvic symphysis, which is crucial during movements.
Understanding the Femur and Its Importance
The femur, known as the longest bone in the human body, is not merely a muscle attachment point; it actively participates in transmitting body weight from the hip to the tibia during daily activities. This unique design, with its oblique position and specialized joints, allows for remarkable stability and strength. Understanding its features, such as the greater and lesser trochanters, can illuminate why certain exercises or motions may impact your fitness and health.
The Tibia and Fibula: Dual Functionality
Adjacent to the femur, the tibia and fibula share a vital partnership, forming the core of the lower leg’s structure. The tibia is thicker and bears the body’s weight, while the fibula serves as a muscle attachment point. This duality exemplifies the intricate balance of our skeletal system, prioritizing both support and mobility. Recognizing the significance of these bones can inspire a deeper appreciation for how we engage in fitness and physical activity.
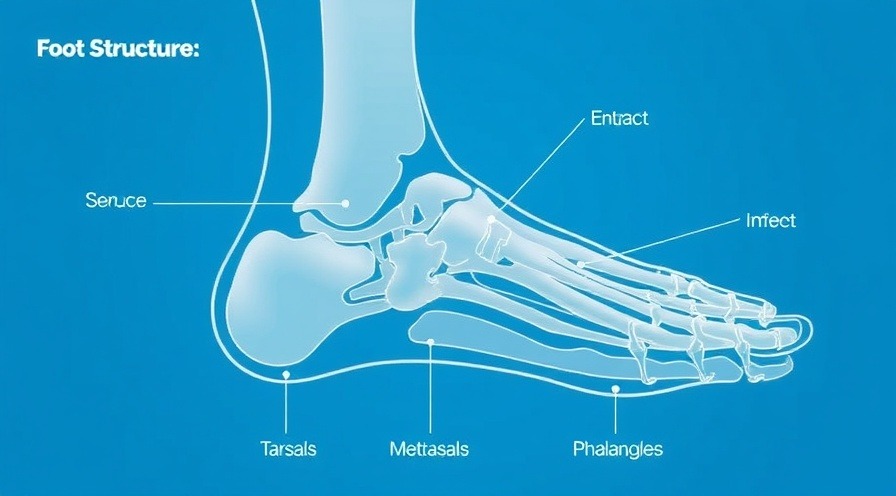
Innovative Foot Structure: Tarsals, Metatarsals, and Phalanges
The foot’s anatomy is a masterpiece comprised of several components: the tarsus, metatarsus, and phalanges. The tarsal bones contribute to the foot's stability, while metatarsals and phalanges allow for dexterity in movement. For health-oriented individuals, understanding how these bones come together to form the foot can emphasize the significance of supportive footwear and proper posture while standing or walking.
Practical Insights for Health and Wellness
Understanding the anatomy of the lower limb is not just an academic exercise; it can transform how health-conscious adults approach their daily habits. From choosing exercises that support skeletal health to understanding why posture affects overall well-being, knowledge is power. Movement patterns, especially those involving the lower limbs, are foundational to maintaining physical health.
By comprehending the rich details of the lower limb skeleton, you empower yourself to make informed decisions about your fitness and health maintenance. Always consult professionals for personalized advice tailored to your needs.
Interested in unlocking your full potential in health and wellness? Explore options that enhance your understanding of human anatomy and your path to fitness and health.
Disclaimer: The information provided on this website is for general informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a qualified healthcare professional before making any decisions or taking actions related to your health, including but not limited to medical conditions, devices, treatments, diets, supplements, or exercise programs. The content on this site is not intended to replace professional medical guidance. The website and its authors are not responsible for any actions taken based on the information provided. Ask your doctor or licensed medical professional first.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 


Write A Comment