Last night, after tossing and turning for hours, I finally cracked the melatonin mystery. If sleepless nights have you desperate, this simple melatonin fix could transform your evenings—letting you finally drift into the restful sleep you’ve been craving. Ready to reclaim your nights?
Unlocking the Power of Melatonin for Sleep: The Essential Guide

Opening Hook: The Melatonin Breakthrough for Restful Nights
If you find yourself staring at the ceiling night after night or waking up far from refreshed, melatonin may seem like the magic bullet for your problems. But melatonin isn’t just another sleep aid; it’s your body’s built-in bedtime cue, anchored deeply in your biology. In this guide, we explore why you might be struggling to get results from melatonin supplements and offer the essential fixes you need for better rest tonight.
Millions turn to melatonin supplements for sleep, seeking a simple answer to their sleep disorders, jet lag, or restless evenings. However, unlocking its real power involves more than grabbing a pill from the store shelf. Here, you’ll uncover how melatonin regulates your circadian rhythm, how to use it properly, and what you must know about possible side effects. The right approach can mean the difference between another restless night and waking up truly restored.
What You’ll Learn About Melatonin and Sleep
Understand what melatonin is and its critical role in sleep circadian rhythm
Discover practical fixes for melatonin struggles, including melatonin supplements
Recognize side effects and optimal use for different sleep disorders
Answers to urgent People Also Ask about melatonin
What is Melatonin? [Definition, Function, and Importance]
How Melatonin Regulates Your Sleep Cycle and Circadian Rhythm
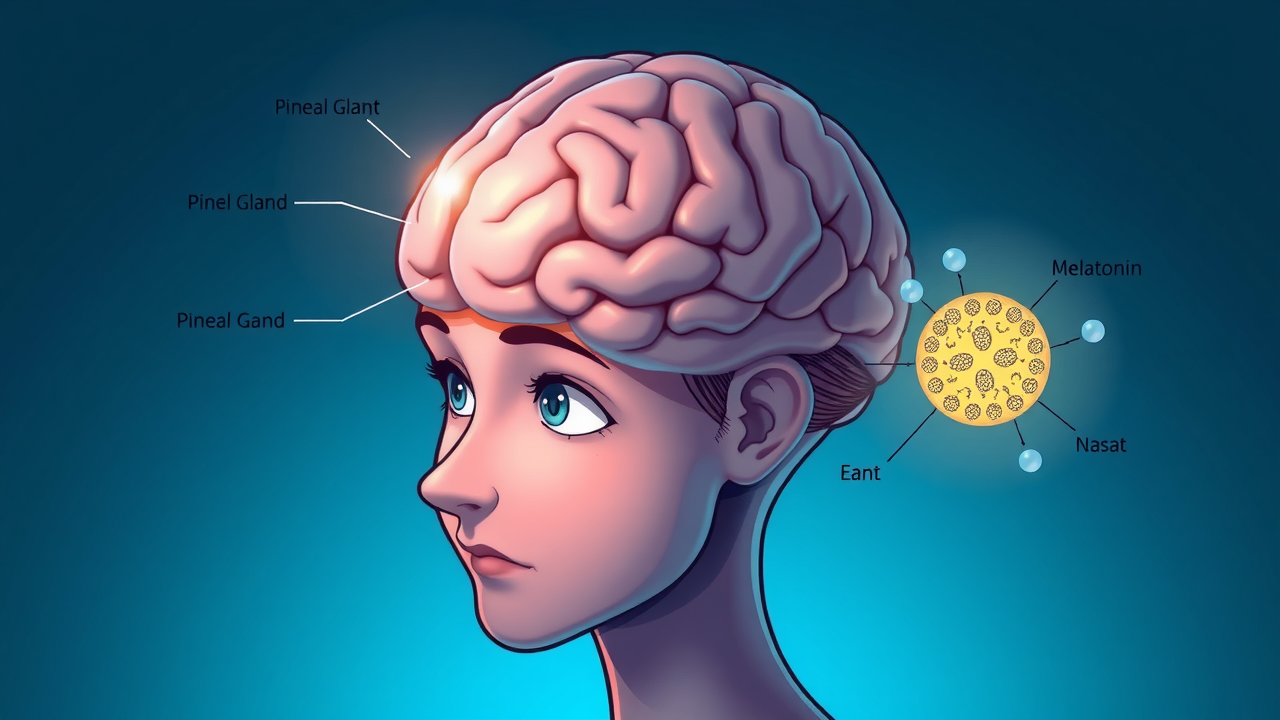

Melatonin is a naturally occurring hormone produced primarily by your pineal gland—a small, pea-sized structure deep within your brain. This “hormone of darkness” is intimately linked to your circadian rhythm, also known as the sleep-wake cycle, acting as a biological signal that helps coordinate your body’s internal clock. As daylight fades, melatonin production ramps up, peaking at night to let your body know it’s time to wind down and fall asleep.
Proper melatonin levels keep your circadian rhythm and sleep phase stable, ensuring you get regular, restorative sleep. When your circadian rhythm is disrupted—by shift work, late-night screens, or travel—melatonin production may falter, leading to sleep problems, delayed sleep phase disorders, or persistent insomnia. Understanding this critical hormone’s role isn’t just useful for those with sleep disorders; it empowers anyone aiming to improve their wake cycle, energy consistency, and long-term wellness.
Melatonin Levels: Natural Production and External Factors
Your natural melatonin levels follow a predictable cycle, rising in the evening and dropping in the daylight. But this rhythm can be pushed off course by a range of factors—late-night screen time, exposure to artificial lights, work schedules, age, and even changes in seasons. While many try to restore balance with melatonin supplements, the real key is learning how both internal and external influences shape your melatonin production. Melatonin supplementation can help, especially for jet lag or those with significant disruptions to their circadian rhythm, but it’s critical to match supplementation to your body’s unique rhythm to get the best results.
Some people naturally produce less melatonin as they age, which may explain increasing sleep problems in older adults. Others, such as shift workers or frequent travelers, may face disruption from constantly changing light exposure. In these cases, understanding and tracking your personal melatonin levels—sometimes with the guidance of a healthcare provider—is a powerful step towards lasting sleep improvements.
Comparison of Natural vs Supplemental Melatonin
eature |
Natural Melatonin |
Supplemental Melatonin |
|---|---|---|
Source |
Pineal Gland (in brain) |
Dietary Supplement (pill, liquid, chewable) |
Timing |
Rises in the evening, falls in morning |
Depends on when you take it |
Optimal Use |
Best when circadian rhythm is healthy |
Best for jet lag, shift work, phase disorders |
Risks/Side Effects |
Rare (unless disrupted by lifestyle or environment) |
Possible drowsiness, vivid dreams, headache, and more (especially if misused) |
Regulation |
Controlled by body’s internal clock |
Regulated as a dietary supplement (not FDA-approved for most uses) |
Melatonin for Sleep: How It Works and Why It Matters
Exploring Melatonin’s Role in Tackling Sleep Disorders

For those struggling with sleep disorders—like insomnia, delayed sleep phase, or jet lag—melatonin offers unique hope. Unlike conventional “sleep meds,” melatonin doesn’t force sedation; instead, it acts as a cue that gently nudges your circadian rhythm back on track. Research shows melatonin supplementation may help you fall asleep faster, adjust to new time zones, or overcome shift work–related sleep problems by correcting the timing of your body’s sleep phase.
Melatonin for sleep is often recommended for short-term use, particularly for resetting your sleep cycle after travel or for shift workers. It’s less effective for chronic insomnia unrelated to circadian disruption but may support those with specific phase disorders or children with autism spectrum disorder. The effects of melatonin on sleep can be noticeable even within a few days of proper use, making it a powerful—and often safer—alternative to more potent sleep medications.
If you’re interested in how sleep disorders beyond insomnia can impact your rest, especially conditions like sleep apnea, you might find it helpful to explore this in-depth look at sleep apnea surgery and its role in restoring healthy sleep patterns. Understanding the broader landscape of sleep health can help you make more informed decisions about your own sleep strategies.
Melatonin Supplements vs Prescription Sleep Medications
When comparing melatonin supplements to prescription sleep medications, it’s essential to know the difference. Prescription sleep meds like benzodiazepines or Z-drugs directly sedate the brain and often carry the risk of dependence or next-day grogginess. Melatonin, on the other hand, is a biological cue that works naturally with your body’s internal processes. While melatonin may not be as immediately powerful as prescription options, it’s typically safer for short- and long-term use—especially for those concerned about side effects or drug interactions.
“Melatonin is the signal our bodies use to tell us it’s time to rest—it’s not just a sleep aid, it’s a biological cue.”
It’s also important to remember that melatonin doesn’t “knock you out” like a sleeping pill. It works best when used at the right time, in the right dose, and as part of a broader approach to sleep hygiene. Those seeking a quick fix should pair melatonin supplements with practical strategies—like consistent sleep schedules and controlled lighting—for optimal results.
Struggling with Melatonin? Root Causes and Fixes Tonight

Common Reasons You’re Not Getting Results from Melatonin Supplements
Incorrect timing or dosage of melatonin supplements
Disruption in circadian rhythm from shift work or travel
Underlying sleep disorders
If melatonin supplements haven’t transformed your nights, you aren’t alone in struggling with effective melatonin use. The most common reason is incorrect timing: taking melatonin too late (or too early) can confuse your circadian rhythm even more. Experts recommend taking melatonin 30 minutes to an hour before your desired sleep time. Dosage also matters; too much melatonin supplement can actually worsen insomnia, making it harder to fall asleep or waking you up in the middle of the night. Most adults need only 0.5mg to 3mg—a much smaller dose than many over-the-counter products offer.
Disrupted routines from shift work, irregular bedtimes, or frequent traveling (hello, jet lag!) can flatten your normal melatonin production. And for some, underlying sleep disorders—like sleep apnea or chronic insomnia—may require targeted treatment beyond melatonin. If your sleep problems persist despite proper supplement use, consult a health care provider to rule out these possibilities and receive personalized guidance.
How to Properly Use Melatonin for Immediate Effect

To maximize benefits and minimize side effects, taking melatonin the right way is crucial. Start with the lowest effective dose (0.5–1mg) about 30–60 minutes before your scheduled bedtime. For jet lag or shift work–related disturbances, time your dose several days before you need to shift your sleep phase, not just the night before. And always read labels: quality matters, and dosages vary widely between brands.
Melatonin for sleep works best when taking melatonin is combined with a consistent bedtime routine. Dim lights in the hour before bed, avoid screens, and keep your bedroom cool, quiet, and dark. If you don’t see results within a week of proper use, it’s time to revisit your approach or talk to your provider about alternative solutions.
Lifestyle, Diet, and Environmental Tips to Boost Melatonin Levels
You don’t always need a supplement to optimize your melatonin production. Simple changes to your daily lifestyle can support your body’s natural rhythm. For instance, exposing yourself to bright sunlight in the morning and dimming lights as evening approaches helps anchor your circadian rhythms. Reducing blue light from screens an hour before bed, eating melatonin-rich foods (like tart cherries, walnuts, and tomatoes), and maintaining a steady sleep-wake cycle can all lead to better natural sleep.
-
Quick Wins for Better Melatonin and Sleep Tonight:
Avoid caffeine and alcohol late in the evening
Practice relaxing activities (reading, light stretching) at night
Keep your sleep environment dark and cool
Use blackout curtains or a sleep mask to block light
Stick to a regular bedtime—even on weekends
With these habits, your body’s melatonin levels will naturally rise at night, leading to better sleep—and, often, no need for extra supplements at all.
Melatonin Side Effects: What You Need to Know
Short-Term and Long-Term Side Effects of Melatonin

While melatonin supplements are generally considered safe for short-term use, they aren’t entirely free from side effects. Some people may experience headaches, dizziness, nausea, or next-day drowsiness. Rarely, vivid dreams or changes in mood have been reported. For most adults, these effects are mild and temporary, especially when using low dosages as recommended. However, it's important to remember that melatonin is a hormone—and altering hormone levels without clear guidance can have unexpected outcomes on your sleep and daytime functioning.
Long-term use of high-dose melatonin supplements is less studied and may carry additional risks. Emerging evidence suggests potential impacts on reproductive hormones, the immune system, and (in rare cases) interactions with other medications. If you find yourself relying on melatonin to sleep every night, check with your healthcare provider to ensure continued safety and rule out underlying issues that may be causing persistent sleep problems.
Who Should Avoid Taking Melatonin?
Certain groups should approach melatonin supplements with caution. Children, pregnant or breastfeeding women, and people with autoimmune disorders or certain neurological conditions are all candidates for special care. Additionally, those taking blood thinners, diabetes medications, or antihypertensive drugs should consult their provider, as melatonin can interact with these medications and exacerbate side effects. As always, if you have any chronic health problem or are taking other medicines, consult your health care provider before starting melatonin supplementation.
People with uncontrolled epilepsy or those recovering from organ transplants may be particularly at risk, since melatonin’s effects on the immune system and neurological function can pose complications. Monitoring by a qualified care provider is a must for these special populations.
Melatonin Supplements: Choosing Quality and Safety
Identifying High-Quality Melatonin (Ingredients, Dosage, and Labels)

With so many melatonin supplements on the market, picking a safe and effective product can be overwhelming. Look for brands that disclose precise dosages and ingredient lists, and avoid those with unnecessary fillers or additives. Check for third-party testing or certification (like USP or NSF) to ensure label accuracy and purity. Remember that higher doses aren’t better—a small, well-timed dose is usually all you need for melatonin’s full benefits.
Label transparency is crucial, especially as dietary supplements are not regulated as strictly as prescription drugs. Product reviews and reports from other consumers can also help you steer clear of unreliable or misleading brands. If you’re concerned about contamination or ingredient quality, choosing melatonin made in GMP-certified facilities can provide extra peace of mind.
The Truth About Melatonin and Blood Pressure
Recent research has explored the possible link between melatonin and blood pressure regulation. While melatonin may have modest blood pressure–lowering effects, especially in those with elevated nighttime blood pressure, the evidence is not yet robust enough to recommend it solely for this purpose. For most people, occasional use of melatonin supplements at low doses does not significantly affect blood pressure. However, if you suffer from hypertension or are taking antihypertensive drugs, consult your doctor before adding melatonin, as combining the two can occasionally lower blood pressure more than intended.
Always discuss ongoing melatonin use with your provider—especially if you’re already managing blood pressure or cardiovascular risks.
Special Considerations: Melatonin and Unique Sleep Needs
Using Melatonin for Shift Work or Jet Lag

For those who regularly travel across time zones or work odd shifts, melatonin can be your best ally in resetting your sleep phase. Taking melatonin about an hour before your new desired sleep time—beginning a few days before your travel or schedule change—can help synchronize your body’s internal clock and ease the transition. Many airline crews, nightshift workers, and business travelers report better adaptation and less jet lag when they use melatonin this way.
Melatonin supplementation for shift work may help you fall asleep during the day after a night shift or prepare for a new rotating schedule by supporting your circadian rhythm. Combine melatonin with strict light exposure control (bright light during wake periods, darkness or eye masks during sleep) for maximal effect. Over time, you may find you need smaller doses as your sleep-wake rhythm adjusts.
Melatonin in Children, Older Adults, and Those with Sleep Disorders

While melatonin use is common in adults, it’s also prescribed in special cases for children—especially those with neurodevelopmental or sleep disorders—and older adults who experience reduced melatonin production. Dosages must be lower and usage closely monitored in these groups to avoid disrupting growth hormones, puberty, or other developmental milestones in children, and to minimize fall risk in seniors.
For patients suffering from delayed sleep phase disorders, mild autism, or certain ADHD sleep complications, melatonin can offer safe and effective relief when used under professional supervision. However, consult a health care provider before giving melatonin supplements to children or older adults to ensure safety and effectiveness tailored to the individual’s health needs.
People Also Ask: What does melatonin do to the body?
Melatonin’s Effects on the Body: Beyond Sleep
Melatonin does more than regulate sleep. As a hormone, it affects many bodily functions: boosting antioxidant defenses, modulating immune cell activity, and even influencing digestive processes in the gut. In recent studies, melatonin has been shown to help regulate seasonal reproduction in animals and support the body’s resilience against oxidative stress. These far-reaching effects of melatonin are still being studied, but they reveal why responsible use is so important—melatonin supplementation is never just about sleep.
Some evidence suggests melatonin helps the body repair damage and fight inflammation, providing systemic benefits that extend beyond the brain. However, these effects depend on proper usage and healthy overall habits.
People Also Ask: Is melatonin safe for pregnant?
Safety of Melatonin Supplement Use During Pregnancy

There is limited research on the safety of melatonin supplementation during pregnancy. While naturally produced melatonin is important for regulating the maternal-fetal sleep cycle, taking supplemental melatonin is not routinely advised unless prescribed by a healthcare provider. Some early evidence suggests possible effects on reproductive hormones, which makes caution and professional consultation critical for expectant mothers considering melatonin for sleep or jet lag.
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, always consult your OB-GYN or health care provider before starting melatonin or any new supplement.
People Also Ask: Is melatonin a sleeping pill?
Is Melatonin a Sleeping Pill? The Key Differences
Melatonin is not a traditional sleep med or sleeping pill. While both may help you fall asleep, sleeping pills generally induce drowsiness or sedation directly, while melatonin acts as a signal for your body’s natural sleep processes by influencing your circadian rhythm. Melatonin helps synchronize your internal clock, while sleeping pills usually override it. This makes melatonin a gentler and more natural option, especially for phase-related sleep issues rather than chronic insomnia.
Those who need a rapid, guaranteed effect may find melatonin less predictable than prescription options but often safer and without the risk of dependency.
People Also Ask: Does melatonin lower blood pressure?
Melatonin and Blood Pressure: What the Research Shows
Several small studies suggest melatonin may have a mild blood pressure–lowering effect, especially at night, but consult your doctor if you have concerns. This is partly due to melatonin’s ability to relax blood vessels in sync with the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle. Still, these effects are not consistent across populations, and melatonin should not substitute for prescribed blood pressure medication. Anyone concerned about blood pressure—especially those with cardiovascular risks—should consult a provider before taking melatonin regularly.
Key Takeaways: Mastering Melatonin for Restful Sleep Tonight
-
Must-Know Tips for Effective Melatonin Use
Take melatonin 30–60 minutes before bedtime, at the lowest effective dose
Anchor your sleep-wake cycle with consistent bed and wake times
Support melatonin’s effects by dimming lights and powering down screens before bed
Choose high-quality, well-labeled supplements or consult a health care provider for personalized advice
Address persistent sleep problems or disorders with professional support

Top FAQs on Melatonin, Side Effects, and Optimal Sleep
Frequently Asked Questions about Melatonin for Sleep
Q: What does melatonin do to the body?
A: Melatonin regulates your body’s sleep-wake cycle and influences other functions such as immune response and antioxidant defenses. It tells the body it’s time to prepare for sleep and helps fine-tune the timing of your sleep phase.Q: Is melatonin safe for pregnant women?
A: Current evidence is limited. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult a health care provider before taking melatonin, as it may affect reproductive hormones and fetal development.Q: Is melatonin a sleeping pill?
A: No, melatonin is a hormone that signals bedtime and regulates circadian rhythms. Sleeping pills induce drowsiness directly and are often more potent but may carry risks of dependency.Q: Does melatonin lower blood pressure?
A: Some evidence suggests melatonin can mildly lower nighttime blood pressure, but it is not a treatment for hypertension. Consult your doctor if you are concerned about interactions with blood pressure medicines.
Conclusion: Your Path Forward to Better Sleep with Melatonin
Final Thoughts on Using Melatonin Safely and Effectively
When used wisely, melatonin can be a powerful tool for conquering sleep problems and restoring a natural rhythm—making restful nights a reality.
If you’re looking to take your wellness journey even further, consider exploring holistic approaches that support not just sleep, but your overall health. For example, learning about holistic remedies for kidney health can provide valuable insights into how interconnected your body’s systems are, and how optimizing one area can positively influence your sleep and vitality. Dive deeper into these strategies to unlock a more balanced, energized you.
Sources
Sleep Foundation – https://www.sleepfoundation.org/melatonin
NIH – Melatonin in Sleep Disorders – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5871173/
To deepen your understanding of melatonin and its role in sleep regulation, consider exploring the following authoritative resources:
“Melatonin: Benefits, Uses, Side Effects, and Dosage” (healthline.com)
This comprehensive article delves into how melatonin functions as a sleep aid, its potential health benefits, recommended dosages, and possible side effects.
“Melatonin: What It Is, What It Does & How It Works” (my.clevelandclinic.org)
Provided by the Cleveland Clinic, this resource offers an in-depth look at melatonin’s biological functions, its impact on the sleep-wake cycle, and guidance on its use as a supplement.
If you’re serious about improving your sleep quality and understanding melatonin’s effects, these resources will provide you with valuable insights and practical advice.
More Health & Wellness can be found here: https://ncwellnesshub.com/
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




Write A Comment