
Struggling with unexplained digestive symptoms? Up to 60% of irritable bowel syndrome cases actually involve some form of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), often misdiagnosed for years.
If persistent bloating, constipation, or diarrhea have left you searching for answers, you may be dealing with either methane SIBO or hydrogen SIBO—two distinct types of intestinal bacterial overgrowth that demand different treatment approaches. In this comprehensive guide, we uncover the key differences in methane SIBO vs hydrogen SIBO treatment differences, practical diagnostic steps, and real relief strategies to help you restore your gut health—starting today.
Unmasking the Hidden Prevalence: Methane SIBO and Hydrogen SIBO in Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth
Many individuals who think they suffer from “regular” irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) are surprised to learn that a sizable percentage—up to 60%—actually have small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. SIBO isn't a one-size-fits-all diagnosis; it comes in different forms, the most common being methane SIBO and hydrogen SIBO. What distinguishes them largely depends on the types of gas produced by gut bacteria that have migrated to the small intestine.
Methane SIBO is commonly associated with constipation-predominant symptoms due to the activity of methanogenic archaea, whereas hydrogen SIBO tends to produce more diarrhea through the overgrowth of hydrogen-producing bacteria. Early breath testing has become the gold standard for diagnosing small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, providing accurate identification of methane and hydrogen SIBO to guide effective, individualized treatment plans. In both cases, understanding the underlying dysfunction is critical to selecting the right treatment and achieving relief from troublesome gastrointestinal symptoms.

Methane SIBO vs Hydrogen SIBO Treatment Differences: Why Understanding Bacterial Overgrowth Types Matters
Recognizing the methane SIBO vs hydrogen SIBO treatment differences is crucial for targeting the root cause of your digestive issues and ensuring successful recovery. Both conditions arise from abnormal overgrowth of intestinal bacteria, but the dominant organisms—methanogenic archaea for methane and various bacteria for hydrogen—respond differently to therapies.
For instance, hydrogen SIBO often improves with a single course of rifaximin, while methane SIBO is typically more stubborn, demanding combination or longer-duration antibiotic regimens. Furthermore, dietary strategies, motility support, and microbiome repair differ based on the SIBO type, making a one-size-fits-all approach ineffective.
This guide offers comprehensive insights into small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, addressing diagnostic nuances, key treatment strategies including the low FODMAP diet and elemental diet, expert advice from SIBO specialists, and practical steps to restore a healthy gut microbiome.
Demystifying Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth: Key Concepts and Causes
Defining Small Intestinal, Intestinal Bacterial, and Gut Bacteria Imbalances
To truly understand methane SIBO vs hydrogen SIBO treatment differences, start with the basics of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. SIBO occurs when populations of intestinal bacteria that should reside primarily in the colon (large intestine) flourish abnormally within the small intestine. This bacterial invasion disrupts normal digestion, impairs nutrient absorption, and triggers troublesome symptoms like bloating, abdominal pain, irregular stools, and more.
Under healthy conditions, only minimal bacterial populations are found in the small intestine, compared to the densely populated colon. The normal small intestine has effective motility, adequate stomach acid production, and immune defenses to limit bacterial growth. However, factors such as repeated antibiotic use, low stomach acid, motility disorders (like IBS), changes in diet, and chronic stress can compromise these defenses, paving the way for overgrowth. Since symptoms of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth often mimic IBS and other gastrointestinal disorders, breath tests are essential for proper diagnosis by experienced healthcare providers.
"The human gut microbiome is as unique as a fingerprint, and imbalances in intestinal bacteria can result in chronic symptoms that are often misdiagnosed." – Leading SIBO researcher

Diagnosing Methane SIBO vs Hydrogen SIBO: The Role of Breath Test and Breath Testing
How Breath Tests Identify Hydrogen and Methane Gas Producers
Accurate diagnosis of specific small intestinal bacterial overgrowth types depends on non-invasive breath tests that measure hydrogen, methane, and hydrogen sulfide gases. These tests measure levels of hydrogen, methane, and occasionally hydrogen sulfide gases in breath samples after the patient ingests a sugar solution (usually lactulose or glucose). As the gut bacteria ferment the sugar, they produce gases, which can be detected and quantified through breath testing equipment. Elevated hydrogen on a breath test typically indicates hydrogen SIBO, while methane signals methane SIBO—often linked to the presence of “methanogen” archaea (mainly Methanobrevibacter smithii).
A diagnostic curve emerges, mapping time to gas concentration. Results are interpreted by measuring a rise in hydrogen and/or methane at specific intervals. However, interpreting breath test data involves nuances: results can be affected by recent antibiotic use, sluggish gut transit, and even improper sample collection.
In addition, a subset of SIBO—hydrogen sulfide—may be missed altogether by standard assays and requires newer, more specialized testing. Working with an experienced healthcare provider or SIBO specialist is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective management.
SIBO Type |
Main Gas |
Diagnostic Breath Test Results |
Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|
Methane SIBO |
Methane (CH4) |
Methane >10 ppm on 2 or more samples |
Constipation, bloating, nausea |
Hydrogen SIBO |
Hydrogen (H2) |
Hydrogen rises ≥20 ppm above baseline within 90 min |
Diarrhea, bloating, cramping |
Hydrogen Sulfide SIBO |
Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) |
Often negative or low hydrogen/methane with “rotten egg” odor |
Gas, pain, sometimes loose stools |
People Also Ask: What is the difference between methane SIBO and hydrogen SIBO?
Methane SIBO involves overproduction of methane by intestinal bacteria and archaea and is typically linked to constipation and slow gut motility.
Hydrogen SIBO produces hydrogen gas, leading to diarrhea and more rapid transit.
Treatments differ: Methane SIBO is often more resistant and may require combinations of antibiotics, whereas hydrogen SIBO often responds to rifaximin alone.
Understanding Bacterial Overgrowth: Differentiating Methane SIBO and Hydrogen SIBO
Small Intestinal Differences: Sources and Symptoms
The key to successful treatment lies in identifying the dominant organisms behind the overgrowth. In methane SIBO, intestinal methanogen overgrowth becomes the problem—unique to methanogenic archaea like Methanobrevibacter smithii. These archaea thrive off excess hydrogen produced by other bacteria, then convert it to methane, which is particularly constipating for the gut.
Hydrogen SIBO, on the other hand, results from an abundance of hydrogen-producing bacteria, such as certain strains of Escherichia coli or other coliforms, producing classic symptoms like bloating, abdominal pain, and rapid-transit diarrhea. Although overlap occurs, symptoms and diagnostic profiles can help steer clinical decisions, with methane SIBO often requiring a more robust or tailored approach.
Hydrogen Sulfide SIBO: The Emerging Third Player
An increasing number of challenging SIBO cases may actually stem from hydrogen sulfide gas produced by specialized bacteria. Hydrogen sulfide SIBO is harder to detect, as traditional breath tests often fail to pick up this gas directly, leading to missed diagnoses. Symptoms include classic SIBO complaints along with potential for “rotten egg” breath, increased sensitivity to sulfur-rich foods, and sometimes more pronounced abdominal discomfort.
Newer advanced testing is making it possible to diagnose and treat this form of SIBO, opening doors for effective, personalized therapy for those not responding to conventional hydrogen or methane SIBO treatments.

People Also Ask: Who is the world renowned SIBO specialist?
Dr. Mark Pimentel is internationally recognized for his research and clinical expertise in SIBO and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, leading innovative studies and treatment advancements at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center.
Comparative Treatments: Methane SIBO vs Hydrogen SIBO Treatment Differences and Their Effectiveness
Antibiotic Approaches: Rifaximin, Neomycin, and Combination Therapies
Rifaximin alone is the standard for hydrogen SIBO, showing high success rates for reducing hydrogen-producing bacteria with minimal systemic absorption.
Methane SIBO often requires a combination of rifaximin and neomycin, as methanogenic archaea are much more robust. Some cases respond to prolonged courses or repeated cycles.
Relapse rates can be high for both types, necessitating a plan for motility support and sometimes functional medicine approaches to lower recurrence risk.
The challenge of treating methane SIBO lies in the hardiness of methanogenic organisms, requiring either a more aggressive antibiotic approach, combination therapies, or longer-duration regimens. By contrast, hydrogen SIBO can often be effectively managed with a single course of rifaximin.
"Methane SIBO requires a more aggressive or combinational approach compared to hydrogen SIBO, owing to the hardiness of methanogenic archaea." – GI specialist
Dietary Interventions: Low FODMAP, Elemental Diet, and Gut Microbiome Repair
The Low FODMAP diet restricts fermentable carbohydrates to help control bloating and reduce fuel for gas-producing bacteria.
The elemental diet serves as an effective treatment for resistant small intestinal bacterial overgrowth cases, delivering predigested nutrition in a low-residue formula that starves harmful intestinal bacteria over a two to three week period.
Restoring the gut microbiome after antibiotic treatment is vital; incorporating resistant starches, targeted prebiotics, and gradually increasing dietary diversity supports sustained remission from bacterial overgrowth.

Overview of Dietary Approaches for Methane SIBO vs Hydrogen SIBO
Dietary Approach |
Methane SIBO |
Hydrogen SIBO |
Elemental Diet Use |
|---|---|---|---|
Low FODMAP Diet |
Reduces symptoms but less effective alone |
Significantly reduces bloating/diarrhea |
Both types may benefit during acute flares |
Elemental Diet |
Use for refractory cases; often effective |
Use if antibiotics fail or with comorbidities |
Both types: 2-3 week regimen |
Gut Microbiome Repair |
Vital after aggressive therapy; supports motility |
Important for reducing relapse risk |
Incremental reintroduction of foods post-diet |
Probiotics, Motility Agents, and Alternative Therapies
Probiotics: Specific strains such as Bifidobacterium infantis are sometimes used to outcompete pathogenic bacteria and restore small intestinal bacteria balance. Some patients with methane SIBO may worsen on probiotics, so personal response tracking is key.
Motility Agents: Medications or supplements that boost gut movement (prokinetics) can prevent SIBO recurrence, essential for patients with underlying motility disorders.
Herbal Antimicrobials: Botanicals like oregano oil, berberine, and allicin may substitute for antibiotics in certain cases, though clinical evidence is still developing.
People Also Ask: What is the best treatment for hydrogen and methane SIBO?
Hydrogen SIBO is best treated with rifaximin alone.
Methane SIBO typically requires a combination of rifaximin and neomycin, possibly with adjunct dietary interventions and motility agents.
Dietary changes, motility support, and the elemental diet may be needed for both types—especially in cases of relapse or incomplete response.
Latest Innovations in Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth Treatments
Emerging Treatments: Hydrogen Sulfide Protocols and Next-Generation Testing
Advanced breath tests can now distinguish hydrogen sulfide from other SIBO gases for more precise diagnosis and tailored therapies.
Personalized medicine approaches using microbiome sequencing allow for targeted therapy based on an individual’s unique bacterial profile.
Novel therapeutics, including microbiome transplantation and next-generation prebiotics, are currently being studied to repair persistent gut dysbiosis and reduce relapse.
-
People Also Ask: What is the latest treatment for SIBO?
Cutting-edge treatments for small intestinal bacterial overgrowth emphasize advanced breath testing for accurate microbial detection, personalized antibiotic and herbal combination therapies, and innovative methods to modulate the gut microbiome for lasting health.
Comparative Summary Table: Methane SIBO vs Hydrogen SIBO Treatment Differences
SIBO Type |
Main Gas |
Diagnostic Method |
First-line Treatment |
Alternative Options |
Relapse Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Methane SIBO |
Methane |
Breath test (methane >10 ppm) |
Rifaximin + Neomycin |
Elemental diet, herbal antimicrobials |
Motility agents, microbiome repair |
Hydrogen SIBO |
Hydrogen |
Breath test (hydrogen rise >20 ppm in 90min) |
Rifaximin |
Elemental diet, herbal options |
Motility support, probiotics |
Patient Stories: Living With Methane SIBO and Hydrogen SIBO
"Understanding whether my SIBO was methane or hydrogen-based completely changed my treatment and quality of life." – Patient testimonial
Real-life experiences reveal just how transformative the right diagnosis and therapy can be. Many patients endure years of distressing symptoms, repeatedly told they have IBS or stress-related GI complaints. Once a thorough breath test finally identified the true problem—be it methane or hydrogen SIBO—treatment shifted from broad-spectrum approaches to personalized care, dramatically improving daily well-being.
Some found that combination antibiotic therapy was the only way to conquer methane SIBO constipation; others reported rapid relief from diarrhea and bloating after a single round of rifaximin for hydrogen SIBO. Still others benefited from the elemental diet or motility agents, illustrating that a tailored approach is key. These success stories underscore the value of proactive testing and individualized care, and they inspire hope for anyone still searching for answers.
Expert Advice: Preventing Recurrence and Maintaining Gut Microbiome Health
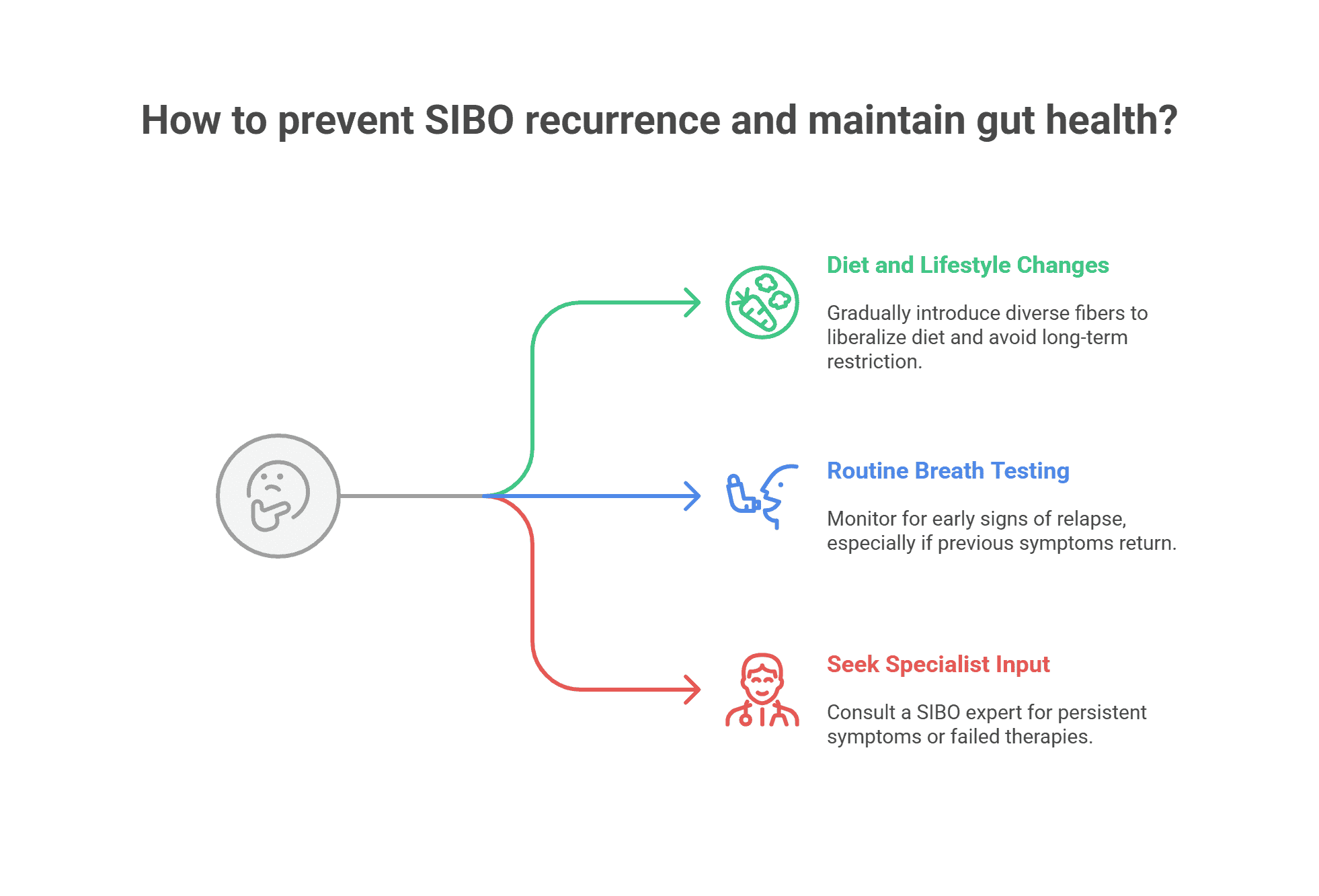
Frequently Asked Questions About Methane SIBO vs Hydrogen SIBO Treatment Differences
Can SIBO types overlap? Yes, some patients have mixed hydrogen and methane overgrowth, requiring combination treatments for both gas types.
How long does it take to treat each SIBO type? Treatment may take 2–4 weeks for hydrogen SIBO, whereas methane SIBO can require several weeks or repeated/combined therapies.
What are the best breath testing intervals post-treatment? Repeat breath testing is usually done 2–4 weeks after treatment and during symptom recurrence.
What dietary changes are essential for long-term recovery? Reintroduce fiber and plant diversity gradually, prioritize a nutrient-dense, minimally processed diet, and use low FODMAP as needed.
Take Control of Your Gut Health: Start Your Methane SIBO vs Hydrogen SIBO Relief Journey Today
Take control of your digestive health by scheduling advanced breath testing, consulting with experienced healthcare providers, and obtaining a personalized treatment plan tailored to your specific small intestinal bacterial overgrowth type. Small steps toward microbiome repair today lead to relief and lasting gut vitality.
Sources:
Cedars-Sinai – https://www.cedars-sinai.org
SIBO Info – https://www.siboinfo.com
NCBI – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5299608/
Gastroenterology Journal – https://www.gastrojournal.org
Recognizing the differences between methane SIBO and hydrogen SIBO is critical for effective treatment strategies and successful management of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth symptoms. Methane SIBO is typically associated with constipation due to the overproduction of methane gas by archaea, whereas hydrogen SIBO often leads to diarrhea as a result of excess hydrogen gas produced by bacteria. Accurate diagnosis through breath testing is crucial, as it guides the selection of appropriate therapies tailored to each SIBO type.
For a comprehensive exploration of these differences, including diagnostic methods and treatment strategies, consider reading The Mysteries and Underdiagnosis of SIBO. This article delves into the complexities of SIBO, highlighting the importance of distinguishing between its subtypes for effective management.
Additionally, What are the Differences Between Methane vs Hydrogen SIBO offers valuable insights into the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for both methane and hydrogen SIBO, aiding in a deeper understanding of these conditions.
If you’re serious about addressing your digestive health, these resources will provide you with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of SIBO and pursue effective relief strategies.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 


Write A Comment