Did you know certain foods can ease seasonal depression symptoms? Nutrient-rich choices like omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin D naturally boost your mood and support mental health.

Discover how simple dietary changes can brighten your winter and support mental health, making tough seasons more manageable and uplifting. In this guide from NCWellnessHub.com, you’ll get actionable insights, evidence-based recommendations, and practical meal ideas to boost your mood throughout the winter season.
Lack of sunlight causes decrease of serotonin, which is placated in mood changes... SAD usually occurs in those who live in areas with prominent winters, shorter days and less sunlight." — Dr. Asim Shah, MD (Professor and Executive Vice Chair in the Menninger Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences at Baylor College of Medicine)
What Are the Top Foods That Help With Seasonal Depression?
If you’re searching for the best foods that help with seasonal depression, focus on leafy greens and other nutrient-dense options that deliver vital folic acid and omega-3 fatty acids linked to improved mental health and a stable mood. Across clinical studies, certain foods show a link to reduced symptoms of seasonal affective disorder (SAD) and the winter blues. These foods work by supporting brain chemistry, balancing serotonin levels, and fueling the body during the colder winter months, when sun exposure is often limited.
Below, we compare the most effective options to help you boost your mood and combat the type of depression that peaks with the change in seasons. Making these whole foods staples in your diet can be a practical and natural way to manage SAD symptoms and improve your mental well-being, especially when paired with other strategies recommended by Our Brand.
Comparison Table: Foods That Help With Seasonal Depression, Key Nutrients, and Mood-Boosting Effects
Food |
Key Nutrient(s) |
Mood-Boosting Effect |
|---|---|---|
Fatty Fish (Salmon, Sardines) |
Omega-3 Fatty Acids, Vitamin D |
Reduces symptoms of seasonal depression, improves serotonin function |
Leafy Greens (Spinach, Kale, Swiss Chard) |
Folic Acid, Magnesium, Iron |
Supports neurotransmitter production, reduces fatigue and low mood |
Citrus Fruits (Oranges, Grapefruits) |
Vitamin C, Flavonoids |
Fights oxidative stress, boosts your mood |
Nuts and Seeds (Walnuts, Chia, Pumpkin) |
Omega-3, Magnesium |
Promotes brain health, stabilizes mood swings |
Eggs |
Vitamin D, Protein, Choline |
Supports mental health and energy levels |
Dark Chocolate |
Polyphenols, Magnesium |
Quickly lifts mood, boosts serotonin levels |
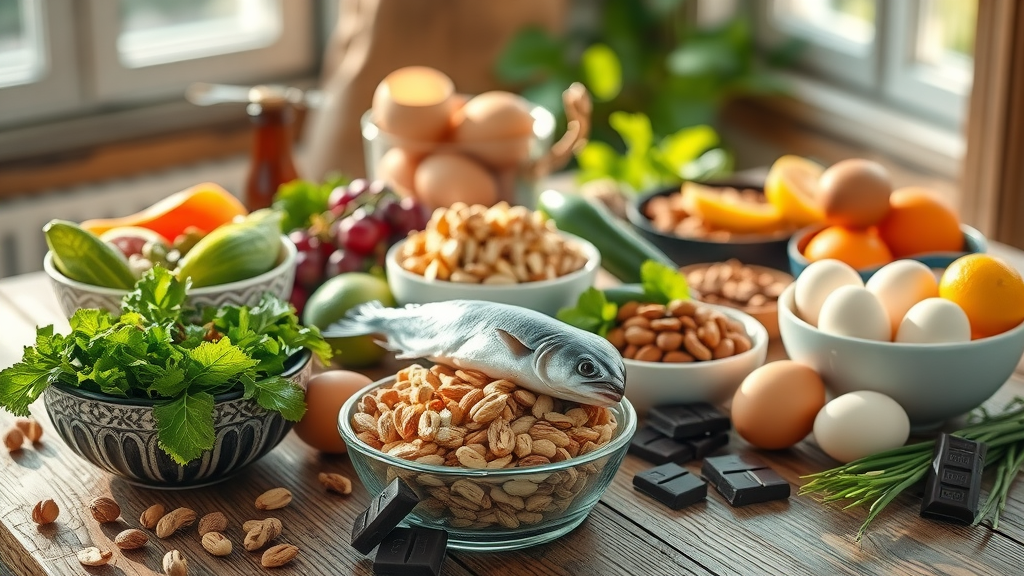

Fatty fish
Leafy greens
Citrus fruits
Nuts and seeds
Eggs
Dark chocolate
"Adding nutrient-rich foods that help with seasonal depression can support mental health throughout the winter months." — Registered Dietitian
While focusing on nutrition is a powerful step, understanding the underlying thought patterns that influence mood can further enhance your approach to managing seasonal depression. For a deeper look at how automatic negative thoughts impact mental health and practical ways to address them, explore this guide to breaking down automatic negative thoughts.
How Do Omega-3 Fatty Acids Affect Your Mood in Seasonal Depression?
Omega-3 fatty acids are crucial nutrients found in select foods that help with seasonal depression and significantly affect your mood by supporting brain chemistry. They have a powerful impact on your brain chemistry and ability to manage stress during the winter blues. Clinical evidence shows that people with lower levels of omega-3s tend to experience more severe symptoms of seasonal affective disorder. Including omega-3-rich foods not only enhances mental health but also stabilizes your mood by supporting healthy levels of serotonin, the neurotransmitter closely tied to happiness and emotional balance.
By incorporating foods rich in fatty acids, such as salmon, sardines, chia seeds, and walnuts, you supply your brain with building blocks it needs to combat the symptoms of seasonal depression. Consuming these foods multiple times per week can make a marked difference in mood—particularly when sun exposure is limited during fall and winter. Our Brand recommends making omega-3s a cornerstone of your winter diet for mental health resilience.
Best Sources of Fatty Acids for Seasonal Depression
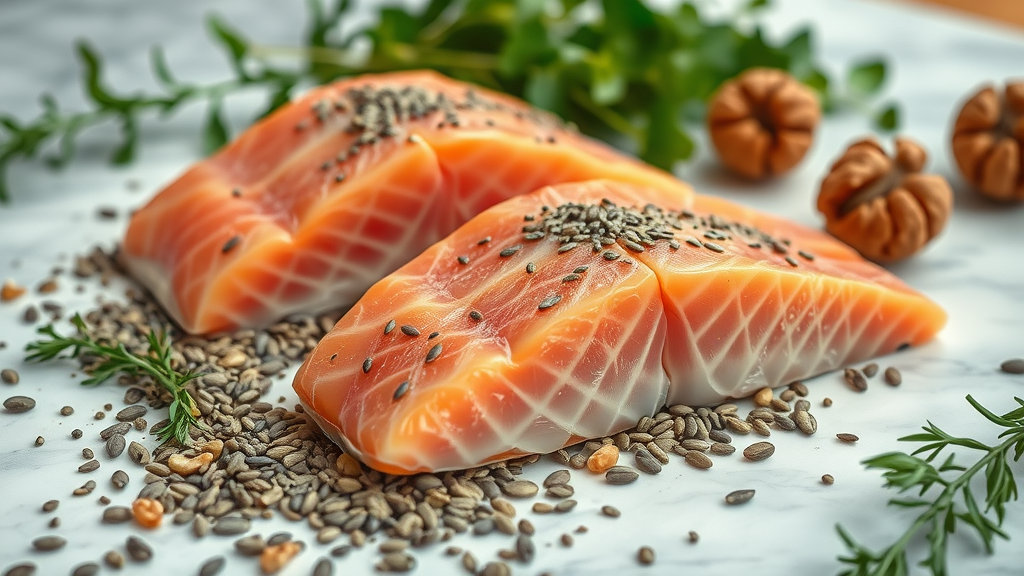

Salmon
Sardines
Chia seeds
Walnuts
These foods offer a great source of omega-3 fatty acids, and studies consistently link them with lowered seasonal depression symptoms and improved mental health outcomes. Try adding a serving of fatty fish or sprinkling chia seeds and walnuts on your salad or oatmeal for a simple boost. Remember, balanced intake is more effective for long-term mental health than high-dose supplements.
"Clinical studies consistently link omega-3 fatty acids with reduced severity of seasonal depression symptoms."
What Role Do Leafy Greens and Folic Acid Play in Easing Seasonal Depression?
There’s growing recognition that leafy greens are among the most vital foods that help with seasonal depression due to their high folic acid content and mood-boosting properties. These vegetables deliver high concentrations of folic acid (also known as folate), which is tied directly to neurotransmitter production, especially serotonin and dopamine. Research suggests that individuals with higher levels of folic acid in their diet are less likely to experience the “winter blues” and other symptoms of seasonal depression.
Leafy greens are also abundant in magnesium and iron, supporting energy metabolism and reducing the fatigue often reported with seasonal affective disorder. Incorporating a variety of these greens—particularly spinach, kale, and Swiss chard—into your meals is an easy and natural way to brighten your mood, especially when sunlight is scarce. At Our Brand, we advocate including leafy green vegetables in salads, omelets, or smoothies for a daily nutrient boost.
How Leafy Greens Boost Your Mood and Support Mental Health
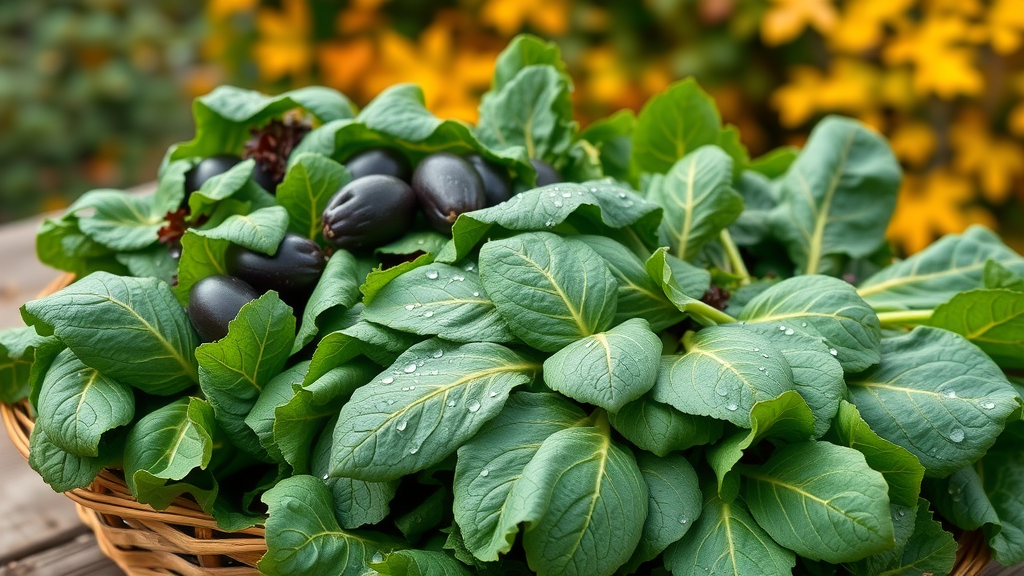

Spinach
Kale
Swiss chard
Table: Folic Acid Content in Popular Leafy Greens and Mood Benefits
Leafy Green |
Folic Acid per Serving |
Mood Benefit |
|---|---|---|
Spinach |
~130 mcg (per 1 cup cooked) |
Aids serotonin production, reduces irritability |
Kale |
~20 mcg (per 1 cup raw) |
Improves energy and focus |
Swiss chard |
~15 mcg (per 1 cup raw) |
Combats mental fatigue, supports calm |
Can Dark Chocolate Genuinely Help With Seasonal Depression?
Yes—dark chocolate is one of the top foods that help with seasonal depression, containing mood-boosting compounds like polyphenols and magnesium that quickly boost your mood. These substances stimulate the release of endorphins and may rapidly boost your mood when enjoyed in moderation. Studies show that consuming dark chocolate can result in measurable improvements in mood and reduction in sad symptoms, especially among those experiencing lower serotonin levels during the winter months.
However, it’s essential to choose dark chocolate (at least 70% cacao) over milk chocolate or sugary confections, as excess sugar can negatively impact blood sugar and mood stability. Our Brand recommends savoring a small portion of high-quality dark chocolate as an afternoon snack or dessert to support mental wellness, without overindulging.
Why Moderation Matters When Eating Dark Chocolate for Mental Health

"Dark chocolate contains compounds that boost your mood — but portion size is key to benefiting your mental health."
While dark chocolate can be a great source of magnesium and help balance blood sugar, consuming too much may cause energy crashes or disrupt sleep due to mild caffeine content. Aim for a serving of 1–2 squares several times per week for optimal effect. The rich flavor and mood-boosting benefits make dark chocolate a satisfying treat as part of an overall diet supporting seasonal depression relief.
How Does Vitamin D From Food Support Mental Health During Seasonal Depression?
Vitamin D deficiency is common during the winter months and is directly linked to increased risk of seasonal depression and winter blues, making vitamin D-rich foods essential for mental health. Getting enough vitamin D is critical for maintaining mental health and supporting the hormone systems that regulate mood. Since sun exposure is far less frequent in colder months, eating foods that help with seasonal depression and are naturally high in vitamin D can fill the gap.
Foods such as egg yolks, fortified cereals, certain mushrooms, and fatty fish are excellent choices to ensure adequate vitamin D intake. Our Brand recommends rotating these foods into your winter meal plans to help maintain serotonin levels and reduce symptoms of seasonal depression. Dietary vitamin D also supports immune function, offering additional protection during the colder months.
Vitamin D-Rich Foods to Include in Your Winter Diet
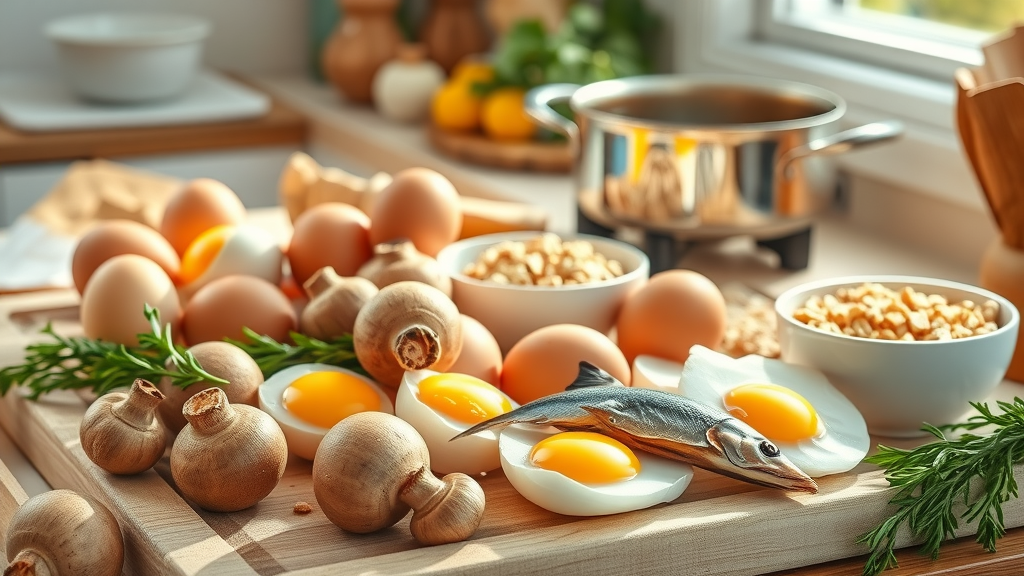

Egg yolks
Fortified cereals
Mushrooms
Fatty fish
Vitamin D from foods is especially valuable for those unable to get regular sun exposure. If you’re experiencing persistent symptoms of seasonal depression, ask your healthcare provider about checking your vitamin D level or adding supplements when dietary intake alone is insufficient.
Do Antioxidant-Rich Foods Help With Seasonal Depression?
Yes—antioxidant-rich produce, including leafy greens and citrus fruits, is an integral part of foods that help with seasonal depression by supporting mental health and reducing oxidative stress. Oxidative stress and inflammation are believed to contribute to symptoms of seasonal affective disorder. Antioxidants work by reducing cellular damage, supporting brain function, and moderating stress. Including a daily mix of berries, citrus fruits, bell peppers, and broccoli supplies vitamins (like C and E), carotenoids, and flavonoids that promote robust mental health and vitality.
You will need to add a variety of these antioxidant-rich foods to every meal—try blueberries and oranges at breakfast, peppers in your lunch salads, and a side of broccoli for dinner—to maintain a healthy mood and cushion your body against the emotional impact of the darker months.
Best Fruits and Vegetables for Antioxidant Support of Mental Health
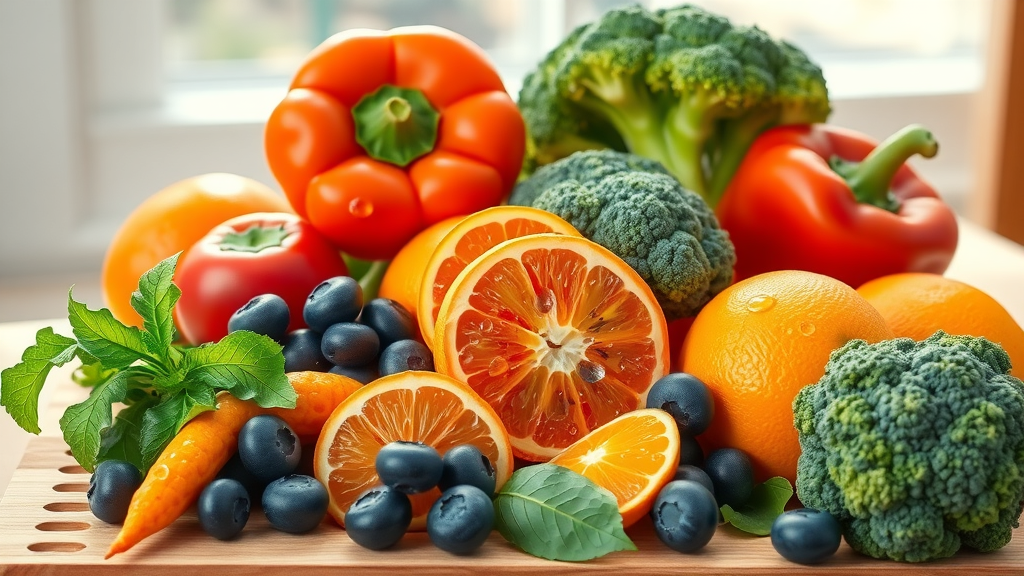

Blueberries
Oranges
Bell peppers
Broccoli
These foods are rich in polyphenols and vitamin C, both linked to improved emotion regulation and lower stress levels. Rotate your selections for maximum benefit and to keep your diet fresh and enjoyable throughout the fall and winter.
How Can Complex Carbohydrates Affect Your Mood and Energy Levels With Seasonal Depression?
Complex carbohydrates stand out among the foods that help with seasonal depression because they provide lasting energy, support balanced blood sugar levels, and positively affect your mood by improving serotonin production. Unlike refined sugary foods and starchy foods that cause rapid spikes and crashes, complex carbs are digested slowly, providing a steady supply of fuel and helping to stabilize mood swings common during periods of lower sunlight.
Top choices—like whole grains, oats, quinoa, and brown rice—are especially effective for managing symptoms of seasonal affective disorder. Including these in your daily meals may not only help combat mental fatigue but also contribute to a positive emotional outlook, according to mounting evidence and consistent guidance from nutritionists.
Table: Complex Carbohydrate Foods vs. Refined Carbohydrates: Impact on Mood
Food Type |
Examples |
Effect on Mood |
|---|---|---|
Complex Carbohydrates |
Oats, quinoa, brown rice, wholegrain bread |
Stabilizes blood sugar, supports serotonin, sustains mood and energy |
Refined Carbohydrates |
White bread, cakes, sugary foods, ice cream |
Causes mood swings, quick energy crashes, increased SAD symptoms |
Whole grains
Oats
Quinoa
Brown rice
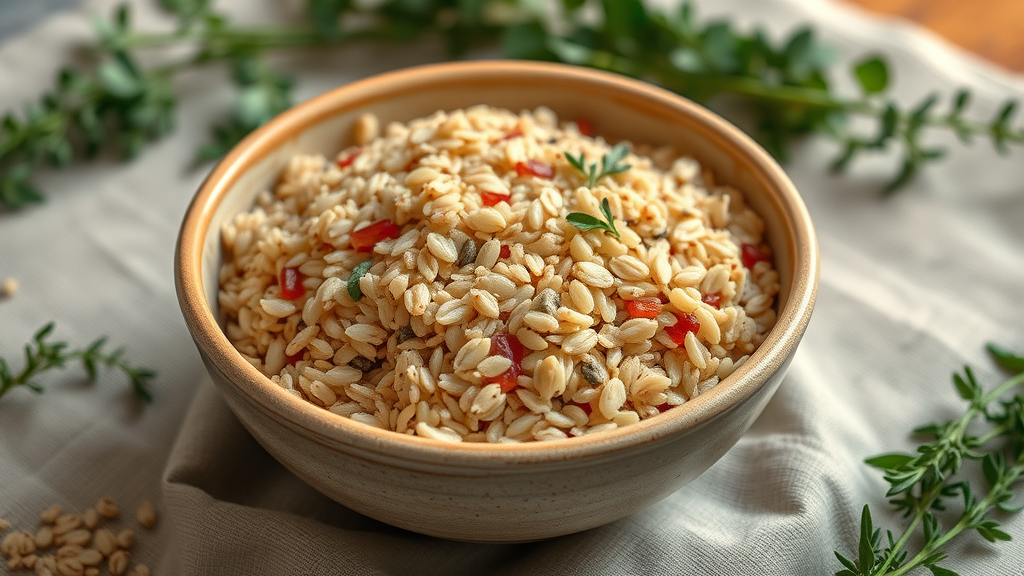

Opt for these whole foods instead of processed and sugary foods, particularly in breakfast and dinner, to foster a more stable mood during the winter months.
What Foods Should You Limit to Reduce Symptoms of Seasonal Depression?
While eating foods that help with seasonal depression is key, it’s equally important to limit foods proven to worsen symptoms of seasonal affective disorder. Processed foods, high in added sugars and unhealthy fats, often disrupt blood sugar and may contribute to mood instability, fatigue, and increased risk of depression. Similarly, excessive caffeine can cause anxiety or sleep disturbances, further aggravating winter blues.
Processed foods
Excess caffeine
Added sugars
Limiting ice cream, sugary baked goods, starchy foods, and high-caffeine drinks can help you maintain more even energy levels and reduce sad symptoms, supporting the benefits of a balanced, whole-food diet as recommended by medical professionals.
How to Create Daily Meal Plans Using Foods That Help With Seasonal Depression
A practical way to incorporate foods that help with seasonal depression is by designing daily meal plans rich in folic acid, omega-3 fatty acids, and dark chocolate to boost your mood and support mental health. Start your morning with an omega-3-rich breakfast (think smoked salmon and eggs), follow up with leafy greens at lunch, and finish your day with an antioxidant-packed dinner featuring colorful veggies and lean proteins.
Breakfast: Smoked salmon on wholegrain toast with a poached egg and sautéed spinach
Lunch: Kale, Swiss chard, and chickpea salad with walnuts, pumpkin seeds, and citrus vinaigrette
Dinner: Broiled trout, roasted sweet potatoes, steamed broccoli, and a square of dark chocolate for dessert
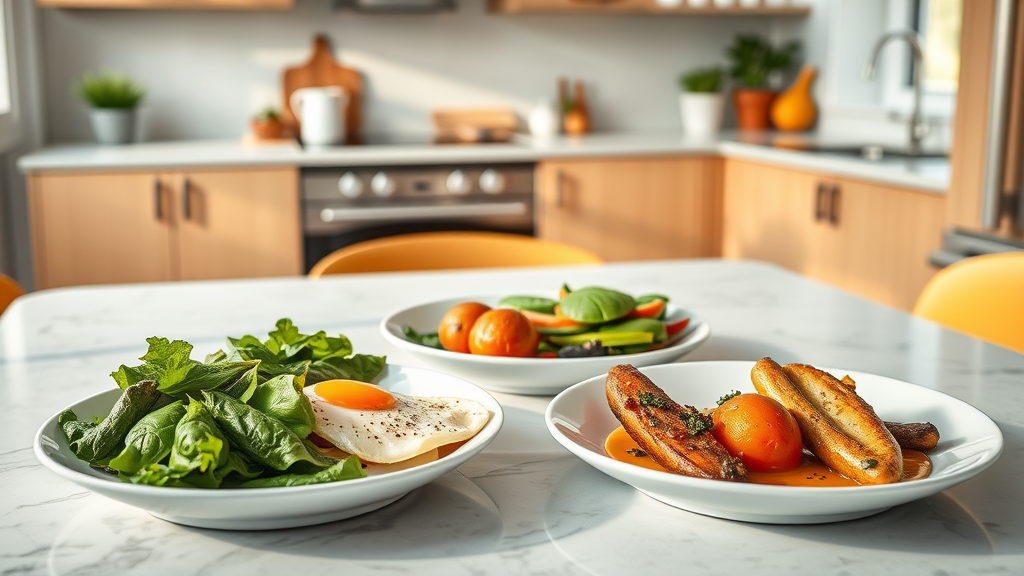

Mix and match these meals. Consistency delivers the best mood-boosting results over time, so try preparing your meals ahead or using a meal kit to simplify winter nutrition.
Are There Case Studies Linking Foods That Help With Seasonal Depression to Improved Outcomes?
Yes, several case studies illustrate the effectiveness of diet in managing symptoms of seasonal affective disorder. These studies involve participants who intentionally increased intake of omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, folate-rich leafy greens, and antioxidants. Results consistently showed improved mood, energy levels, and reduced sad symptoms when such foods became a consistent part of their diets.
The case study summaries below, underscore not only improvements in mood but also in motivation, focus, and social engagement, especially when dietary changes were paired with lifestyle measures (like light therapy and exercise).
Summary of Key Case Studies on Diet and Seasonal Depression Improvement
Study Focus |
Dietary Change |
Reported Outcome |
|---|---|---|
Omega-3 Intake in SAD |
Increased fatty fish (3x/wk), walnuts, chia |
Lower depression scores, stabilized mood |
Vitamin D Supplementation |
Eggs, fortified foods, fish |
Improved energy, fewer episodes of low mood |
Leafy Greens and Folate |
Daily spinach/kale salads |
Fewer sad symptoms, better focus |
"Participants experienced marked mood improvements when including foods that help with seasonal depression." — Study Review
What Lifestyle Factors Work With Foods to Improve Seasonal Depression?
In addition to prioritizing foods that help with seasonal depression, certain lifestyle factors can further minimize symptoms of seasonal affective disorder and the winter blues. Regular exercise, exposure to bright light (light therapy), and a consistent sleep schedule all play key roles in supporting neurotransmitter balance and psychological resilience.
Regular exercise
Light therapy
Consistent sleep schedule
We suggest talking to your doctor first. Typically a holistic approach—combining a nutrient-dense diet with these positive habits—to maximize relief from SAD symptoms and set the stage for a brighter, healthier winter.
This video demonstrates step-by-step how to prepare a nutrient-packed meal using fatty fish, leafy greens, antioxidant fruits, and whole grains—showcasing practical skills to boost your mood naturally during the winter season.
How to Combat Holiday Blues?
Immediate Strategies to Boost Your Mood During the Holiday Blues
To quickly combat mood dips during the holiday season, especially when experiencing the winter blues, focus on eating balanced meals rich in the nutrients outlined above, maintain social connections, and practice self-care routines like mindfulness or relaxing activities. These steps support both immediate mood elevation and long-term mental health according to experts.
Eat balanced meals
Stay socially connected
Practice self-care
People Also Ask: What Foods Are Good for SAD Mood?
Top Mood-Boosting Foods for SAD: Evidence-Based List
Oily fish
Berries
Whole grains
Dark leafy greens
Dark chocolate
These foods have been linked in studies to improved neurotransmitter levels, reduced stress markers, and better overall emotional balance, making them smart daily choices for those managing seasonal affective disorder.
People Also Ask: What Is the Best Food to Improve Mood?
Quick-Acting Foods Proven to Improve Mood
Salmon
Pumpkin seeds
Bananas
Dark chocolate
These options contain mood-enhancing nutrients such as omega-3s, magnesium, and tryptophan (a serotonin precursor). Try them for a quick boost during low-energy periods.
FAQs About Foods That Help With Seasonal Depression
Can changing my diet alone improve seasonal depression symptoms?
Dietary changes, especially increasing foods that help with seasonal depression, can significantly improve mood and energy. However, optimal results often require a holistic approach—combining nutrition with light therapy, exercise, and (if needed) professional support.Which specific nutrients are most important for mood?
Omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, folic acid, magnesium, and antioxidants are crucial for maintaining healthy serotonin levels and regulating stress. Including a range of whole foods ensures you cover all key nutrients.How soon will I notice effects from dietary changes?
Many people report subtle improvements within a week or two, though the biggest benefits typically emerge after sustained changes over several weeks. Consistency with whole foods is essential for long-term mental health gains.
Key Takeaways on Choosing Foods That Help With Seasonal Depression
Consistent dietary habits matter
Nutrient diversity is key
Whole foods offer the greatest benefit for seasonal depression relief
Watch our expert-led video for real-world meal planning tips, ingredient swaps, and easy prep methods to keep your winter nutrition on track—all science-backed, practical, and tailored for you.
What Should You Do Next If You Want to Use Foods That Help With Seasonal Depression?
Speak with a qualified nutrition expert for personalized food plans
Use online resources for meal ideas
Try our branded meal kits for managing the winter blues
By taking these steps, you’ll be empowered to use foods that help with seasonal depression to support your well-being all winter long.
Conclusion
Make simple yet meaningful food choices this winter—emphasizing omega-3s, vitamin D, folic acid, antioxidants, and whole grains—to brighten your mood and protect your mental health.
If you’re ready to take your mental wellness journey even further, consider exploring how emotional awareness and self-reflection can complement your nutritional strategies. Unpacking your emotions is a powerful way to build resilience and foster a healthier mindset, especially during challenging seasons.
Discover actionable techniques and deeper insights in this resource on enhancing well-being through emotional understanding. By combining mindful eating with emotional growth, you can create a holistic foundation for lasting mental health and a brighter outlook all year round.
Sources
Incorporating specific foods into your diet can play a significant role in alleviating symptoms of seasonal depression. For instance, the article “5 Foods and Recipes to Keep Your Seasonal Depression at Bay” from VCU Health highlights the benefits of consuming citrus fruits, leafy greens, dark chocolate, fatty fish, and nuts. These foods are rich in essential nutrients like vitamin D, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants, which can help boost mood and energy levels during the winter months. (vcuhealth.org)
Similarly, the U.S. News article “Foods and Activities to Fight Seasonal Depression (SAD)” emphasizes the importance of vitamin D-rich foods such as salmon, mushrooms, and fortified dairy products. It also discusses the mood-enhancing properties of complex carbohydrates found in whole grains and the benefits of fermented foods for gut health, which is closely linked to mental well-being. (health.usnews.com)
By integrating these nutrient-dense foods into your daily meals, you can support your mental health and combat the effects of seasonal depression.
Support is Here 💜
If you or someone you know is in crisis and needs immediate support, help is available.
In the U.S., you can contact the National Suicide and Crisis Lifeline instantly by calling or texting 988. You can also use the confidential online chat at: 988lifeline.org.
Your well-being matters, and help is just a call, text, or click away.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment