"Did you know that certain osteoarthritis food supplements can reduce pain and improve joint mobility by up to 40%? Discover how these natural solutions can transform your daily comfort and help you regain an active lifestyle starting today."

The Promise of Osteoarthritis Food Supplements
Osteoarthritis is one of the most common joint disorders worldwide, often making everyday activities challenging due to joint pain and stiffness. The growing interest in osteoarthritis food supplements has opened new doors for those searching for natural, effective strategies to reduce pain and restore comfortable, active living. With advances in scientific research, dietary supplements targeting osteoarthritis symptoms are now backed by robust clinical trial and systematic review data, showing encouraging results for pain relief, mobility, and function.
If you or someone you love is dealing with knee osteoarthritis, arthritis pain, or inflammation that disrupts daily life, this guide is your roadmap to understanding how food supplements can fit into comprehensive arthritis care. We'll examine which dietary supplements work, review potential side effects, offer best practices for safety, and highlight evidence from controlled trials, giving you the tools to take control of your joint health journey.
What You'll Learn About Osteoarthritis Food Supplements
The science behind osteoarthritis food supplements
Benefits for treating osteoarthritis symptoms
Clinical trial evidence and systematic review highlights
Potential side effects and safety considerations
Best osteoarthritis dietary supplements and foods
Understanding Osteoarthritis: Symptoms, Causes, and Impact
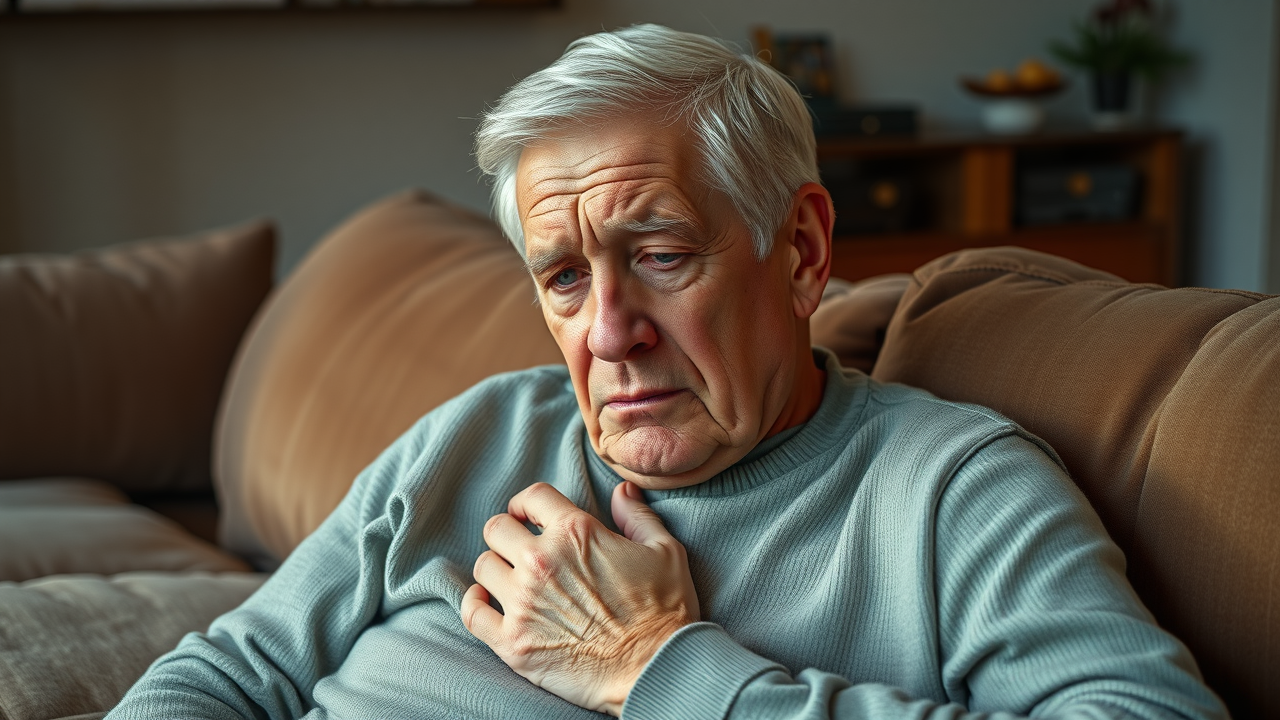

Osteoarthritis Symptoms and Their Effects on Physical Function
Osteoarthritis is defined by the gradual breakdown of cartilage and changes in the underlying bone, predominantly affecting the knees, hips, and hands. Common osteoarthritis symptoms include persistent joint pain, stiffness, limited range of motion, and swelling. These symptoms dramatically impact physical function, making it difficult for individuals to walk, climb stairs, or even perform routine tasks like dressing or cooking. According to recent systematic review findings, pain and function loss can progress without proper management, highlighting the immense importance of early intervention and ongoing care.
Many people with knee osteoarthritis experience pronounced joint pain, especially after long periods of inactivity or repetitive movements. This not only interrupts daily routines but can also jeopardize independence and emotional well-being. Understanding the full spectrum of arthritis symptoms—beyond pain and stiffness—and how they relate to joint health empowers patients to seek targeted, evidence-backed treatments and dietary supplement interventions that go beyond standard care res routines.
Knee Osteoarthritis and Joint Pain: A Closer Look
Knee osteoarthritis is the leading cause of disability among adults. The knee’s weight-bearing role subjects it to constant stress, which accelerates cartilage breakdown and increases the risk of pain and injury. Unlike rheumatoid arthritis, which is autoimmune in nature, osteoarthritis stems from wear, tear, and age—though genetics and prior injuries play roles as well. Recent clinical trial evidence underscores that dietary supplements such as glucosamine and chondroitin or omega-3 fatty acids may help support knee joint health, offering tangible benefits in reducing pain and enhancing mobility.
Through a combination of supplements, improved diet, exercise, and medical interventions, people with knee osteoarthritis can rebuild confidence in daily movement. The right nutritional choices and dietary supplements are essential components in the comprehensive care for those seeking to minimize knee pain and maximize function.
The Role of Inflammation and Arthritis Symptoms
Inflammation is at the heart of osteoarthritis progression. While osteoarthritis is often considered “non-inflammatory,” low-grade inflammation of the joint lining and surrounding tissues contributes to cartilage breakdown and exacerbates arthritis symptoms. Fatty acids such as EPA and DHA found in fish oil and other anti-inflammatory dietary supplements have been studied extensively for their ability to reduce inflammation and, by extension, pain and stiffness in arthritis care.
The connection between chronic inflammation, arthritis symptoms, and physical function is now well established. Properly chosen osteoarthritis food supplements can target these pathways to not only relieve discomfort but also slow the condition’s progression. Addressing both inflammation and biomechanical stress with a combination of diet, supplements, and movement is the gold standard for modern osteoarthritis management.
The Science Behind Osteoarthritis Food Supplements
What Are Dietary Supplements for Osteoarthritis?
Dietary supplements formulated for osteoarthritis support joint health, manage pain, and neutralize inflammation. Common ingredients in these food supplements include glucosamine, chondroitin, omega-3 fatty acids, turmeric/curcumin, vitamin D, and MSM (Methylsulfonylmethane). These nutrients may be found singly or in combination formulas designed to target specific arthritis symptoms. The best osteoarthritis dietary supplements are informed by decades of systematic review and clinical trial data, with each component offering unique benefits in reducing pain or supporting cartilage repair.
While no dietary supplement can reverse damage already done, regular use—often in concert with medical therapies—has shown promise in improving quality of life and restoring physical function for many individuals affected by osteoarthritis pain and stiffness. As with all dietary supplements, efficacy varies based on formulation, dose, and the individual’s health profile, so choosing evidence-backed products and integrating them strategically into a balanced diet is critical.
For those particularly interested in the role of turmeric and curcumin in joint health, you may find it helpful to explore a deeper dive into the daily health benefits of turmeric and curcumin supplementation, which further explains their anti-inflammatory effects and practical usage for arthritis relief.
How Osteoarthritis Food Supplements Can Help: Systematic Review Insights
Robust research—including systematic review analysis and randomized controlled trials—supports the use of certain osteoarthritis food supplements for pain relief, inflammation control, and slowing functional decline. For example, studies have demonstrated that glucosamine and chondroitin can support cartilage health and provide sustained pain reduction for people with knee osteoarthritis. Omega-3 fatty acids, especially EPA and DHA, are recognized for their potent anti-inflammatory properties, which directly address the inflammatory processes underlying arthritis pain.
Turmeric (curcumin) and vitamin D supplements are increasingly gaining attention for their role in treating osteoarthritis. Turmeric’s ability to reduce inflammation has been confirmed across clinical trial and systematic review findings, while adequate vitamin D levels are associated with better joint health, bone strength, and slower disease progression. Below is a summary table highlighting the main dietary supplements, their benefits, and supporting clinical evidence.
Supplement |
Main Benefit |
Clinical Evidence |
|---|---|---|
Glucosamine and Chondroitin |
Joint pain relief and repair |
Supported by randomized controlled trials |
Omega-3 Fatty Acids |
Reduce inflammation |
Documented in clinical trials |
Turmeric/Curcumin |
Anti-inflammatory effect |
Backed by systematic review data |
Vitamin D |
Bone and joint health |
Recommended in controlled trials |
Popular Osteoarthritis Food Supplements: Types and Effectiveness
Glucosamine and Chondroitin for Treating Osteoarthritis

Glucosamine and chondroitin are two of the most thoroughly researched dietary supplements for osteoarthritis. Taken together, they aim to reduce pain and enhance cartilage repair in affected joints. Clinical trial findings suggest that these food supplements are particularly effective for people with knee osteoarthritis, often offering measurable improvements in joint pain, flexibility, and physical function after several weeks of use.
Glucosamine hydrochloride is often used in these products, while chondroitin adds a further layer of support to cartilage and connective tissue health. While some controlled trials note modest results, others highlight significant pain relief and restored movement—especially when dietary supplements are used consistently and in conjunction with medical care and physical therapy.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Their Role in Arthritis Care
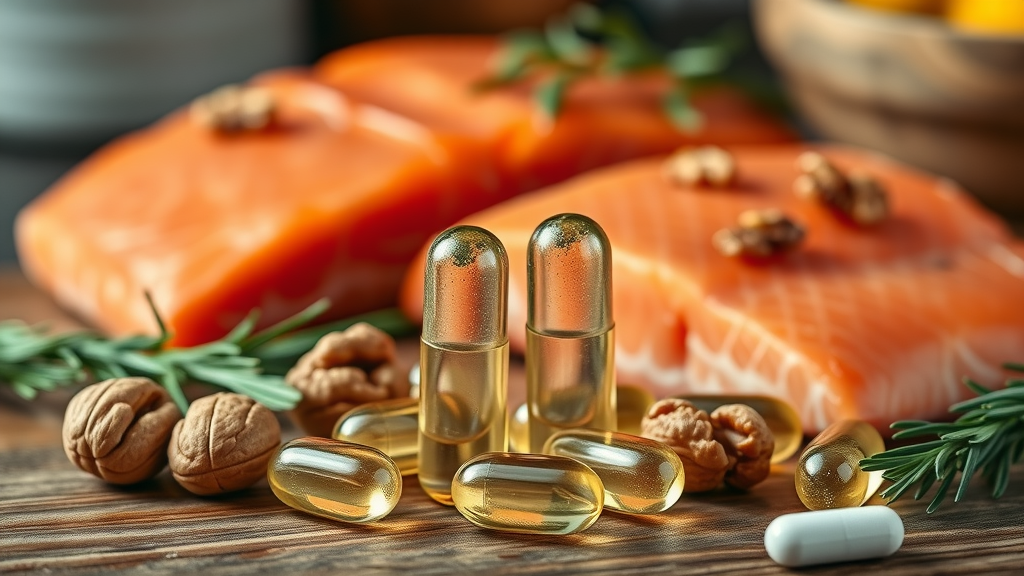

Omega-3 fatty acids (especially EPA and DHA from fish oil) are well-known for their anti-inflammatory powers. These essential fatty acids help block inflammatory pathways within the joint, supporting pain relief and improved mobility for those with osteoarthritis. Research from systematic review articles and clinical trial evidence consistently shows that omega-3 supplementation can reduce joint swelling, pain, and morning stiffness.
For people managing knee osteoarthritis, the addition of fatty acid supplements to the diet can be a game changer. Foods rich in omega-3s—like salmon, walnuts, flaxseed, and chia seeds—also support joint health and can be combined with dietary supplement regimens for broader arthritis care benefits. As always, optimal results rely on regular use and integrating these approaches into an overall strategy focused on reducing pain and protecting long-term joint function.
Other Dietary Supplements for Arthritis Pain and Stiffness
Collagen
MSM (Methylsulfonylmethane)
Turmeric
Vitamin D
Green Tea Extract

In addition to glucosamine, chondroitin, and omega-3s, several other dietary supplements have emerged as helpful for osteoarthritis care. Collagen supplements support your body’s natural ability to rebuild connective tissue and cartilage, while MSM is praised for its potential to reduce pain and stiffness through anti-inflammatory mechanisms. Turmeric (specifically curcumin) has substantial anti-inflammatory effects that help lessen daily arthritis symptoms.
Vitamin D’s importance cannot be overstated, as deficiency is linked to increased risk for worsening osteoarthritis symptoms. Green tea extract delivers natural antioxidants that may further support joint health and provide comfort for those experiencing chronic pain and stiffness. Controlled trials and systematic review data underline the importance of integrating these supplements responsibly, always considering side effects and your personal health status.
Comparing Dietary Supplements: Randomized Controlled Trial Results
"Not all supplements offer the same level of benefit—systematic reviews and clinical trials are essential for separating fact from fiction."
While the supplement market is crowded, randomized controlled trials and systematic reviews help sort fact from fiction. For instance, meta-analyses and controlled trial studies frequently endorse the effectiveness of glucosamine and chondroitin for knee osteoarthritis, while omega-3 fatty acids consistently demonstrate clinically meaningful impacts in reducing pain and inflammation. By contrast, some over-the-counter products lack sufficient data or show mixed results when rigorously tested.
Always prioritize supplements with robust clinical backing, use them alongside medical guidance, and be skeptical of claims not supported by large-scale, well-conducted studies. The most impactful arthritis care approaches combine proven supplements with healthy lifestyle choices, exercise, and a balanced diet for holistic joint health and improved physical function.
How to Incorporate Osteoarthritis Food Supplements into Your Diet
Combining Osteoarthritis Food Supplements with Healthy Foods

Maximizing benefits from osteoarthritis food supplements is easiest when combined with whole foods that support joint health. Begin by incorporating fatty fish (salmon, sardines), leafy greens, berries, and healthy fats such as olive oil and nuts into daily meals. These nutrient-rich foods are naturally anti-inflammatory and can amplify the pain-relief effects of dietary supplements such as fish oil and turmeric. For example, pairing omega-3 supplements with a meal rich in other fatty acids can further enhance absorption while providing a broader range of micronutrients that benefit bone and connective tissue.
Foods high in antioxidants—such as citrus, broccoli, blueberries, and green tea—help control chronic inflammation, reduce pain and stiffness, and protect cartilage from free radical damage. Use supplement powders (like turmeric or collagen) in smoothies or sprinkle them over salads and grains for taste and therapeutic benefit. The key is consistency, strategizing your meals and supplement intake for round-the-clock arthritis care.
Recommended Dosages and Best Practices for Safety
Each dietary supplement has an optimal dosing range best determined by age, overall health, and the severity of osteoarthritis symptoms. For glucosamine and chondroitin, studies often use daily totals of 1,200–1,800 mg. Omega-3 fatty acid supplements (fish oil) are commonly used at 1,000–3,000 mg a day of combined EPA and DHA, while turmeric dosages for arthritis care typically range from 500–2,000 mg per day. Vitamin D supplemental needs vary, but 800–2,000 IU daily is standard, with higher dosages monitored by a healthcare provider.
The most important safety step is to speak with your doctor or pharmacist before starting new supplements, especially if you are on medications or have chronic conditions. Taking more than the recommended amount can lead to side effects such as digestive upset, blood thinning, or interactions with prescription drugs. Always purchase high-quality, third-party-tested supplements for purity and potency, ensuring the best results for pain relief and long-term joint health.
Dietary Supplements vs. Prescription Medications for Arthritis Care
Dietary supplements and prescription medications approach arthritis care in distinct ways. Supplements target the underlying nutritional gaps, support joint repair, and address inflammation at its source, whereas prescriptions like NSAIDs and corticosteroids offer fast, targeted pain relief but often come with greater risk of long-term side effects. In many cases, people with knee osteoarthritis or widespread arthritis pain benefit from a combination approach, using supplements as first-line prevention and prescriptions as needed for severe flare-ups.
Recent clinical trial and controlled trial research supports combining supplements (especially omega-3 fatty acids and glucosamine/chondroitin) with conventional care to minimize drug dependency, manage pain and stiffness, and promote sustained improvements in physical function. Always consult your healthcare provider before adjusting your medication or supplement regimen to develop a personalized, safe arthritis management plan.
Potential Side Effects and Safety of Osteoarthritis Food Supplements
Understanding Side Effects of Popular Dietary Supplements

While osteoarthritis food supplements are generally safe, some can cause side effects—particularly when used at high doses or combined with certain medications. For example, glucosamine and chondroitin may occasionally cause digestive upset, while fish oil might increase bleeding risk especially if taken with blood thinners. Turmeric is safe for most, but high doses can lead to stomach discomfort or, rarely, kidney stones. As with any dietary supplement, individual tolerance varies, and those with multiple health concerns must be especially vigilant.
Quality matters: choose reputable brands that undergo third-party testing to reduce contamination risk. Watch for warning signs such as persistent digestive issues, allergic reactions, or easy bruising, and always report unusual symptoms to your healthcare provider. Side effects are less common at standard dosages, but err on the side of caution and avoid high-dose regimens unless specifically prescribed.
When to Consult with Healthcare Professionals for Arthritis Treatment
You should always engage your healthcare professional before making changes to your osteoarthritis management plan, particularly when adding new supplements or if you’re taking other medications. Signs you need immediate advice include unexpected side effects, worsening pain, or symptoms of drug interactions like abnormal bleeding. Your provider can run appropriate lab tests, check for vitamin deficiencies (such as vitamin D), and guide you in choosing evidence-based, personalized supplement strategies in alignment with controlled trial data.
Remember, individualized care—combining medical treatments, healthy habits, and dietary supplement regimens—offers the greatest potential for improving joint health and reducing arthritis symptoms long-term. Don’t hesitate to seek professional advice and ongoing monitoring for safety and optimal outcomes.
Evaluating Research: Systematic Reviews, Clinical Trials, and Controlled Trials
Latest Findings: Randomized Controlled Trials
Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) remain the gold standard for evaluating the safety and effectiveness of osteoarthritis food supplements. Recent RCTs have demonstrated statistically significant benefits of glucosamine and chondroitin for reducing knee pain and improving joint function, while omega-3 supplements show promise in cutting both pain and stiffness, especially in people with knee osteoarthritis. Turmeric supplementation continues to be validated for its anti-inflammatory effects and safety profile.
It’s worth noting that not all supplements perform equally across studied populations, but the strongest evidence supports consistent use of omega-3 fatty acids, glucosamine/chondroitin, and vitamin D for osteoarthritis symptom management. Always look for supplements that have been evaluated in robust RCTs and make decisions based on the most current scientific evidence.
Interpreting Systematic Reviews for Osteoarthritis Food Supplements
Systematic reviews pool data from numerous clinical trials, offering the most reliable perspective on which supplements work best for treating osteoarthritis. These reviews clearly show trends: for example, glucosamine and chondroitin outperform placebo for knee osteoarthritis pain relief in most populations, while omega-3 fatty acids dramatically reduce inflammation and slow the progression of arthritis symptoms. Some reviews highlight the benefits of MSM and turmeric, though more studies may be needed for long-term effects.
Systematic review findings should always guide your decisions about using dietary supplements for arthritis care, emphasizing products with solid evidence, minimal side effects, and well-defined dosing.
How Evidence Guides Physical Function and Arthritis Symptom Management
The overarching message from both clinical trial and systematic review research is this: evidence-based use of osteoarthritis food supplements can help preserve physical function, reduce pain and stiffness, and improve overall quality of life. Supplements are not replacements for medical management but serve as vital tools within a comprehensive arthritis care approach. The greatest gains in pain relief and joint performance are seen when supplements are combined with exercise, weight management, and anti-inflammatory diets.
Consult with your healthcare provider, track your progress, and continue monitoring new research to ensure your supplement choices remain aligned with evolving best practices.
People Also Ask: Osteoarthritis Food Supplements
Explainer video: How osteoarthritis food supplements support joint health and ease pain, including animations of supplement absorption and testimonials from people with osteoarthritis.
What's a good supplement to take for osteoarthritis?
Glucosamine, chondroitin, omega-3 fatty acids, and turmeric are among the top supplements supported by evidence for osteoarthritis. Always consider consulting a healthcare provider to find the supplement suited to your individual symptoms.
What are the 10 best foods for osteoarthritis?
Top foods include fatty fish, berries, leafy greens, nuts, seeds, olive oil, broccoli, green tea, citrus fruits, and whole grains—each supporting joint health and reducing inflammation.

What vitamin deficiency is associated with osteoarthritis?
Vitamin D deficiency is frequently linked with osteoarthritis and may worsen symptoms or progression; vitamin C and K are also important for joint and bone health.
Do osteoarthritis supplements work?
Evidence varies, but systematic reviews and randomized controlled trials show certain osteoarthritis food supplements do improve pain and physical function for many sufferers.
FAQs: Osteoarthritis Food Supplements
Are these supplements safe with my medications?
Many osteoarthritis food supplements are generally safe but some can interact with prescription medications. Always check with your healthcare provider before starting new supplements to avoid negative drug interactions or increased side effects.How soon can I expect to notice improvement?
Improvements in pain relief and physical function can begin within 2–4 weeks of consistent supplement use, though maximum benefit may take up to three months. Everyone responds differently depending on supplement type and overall health.Can I take multiple supplements for osteoarthritis at once?
Combining several supplements is common, but review your plan with a healthcare professional to ensure safe dosages and avoid additive side effects or unnecessary overlap between products.What are the warning signs of side effects?
Warning signs can include stomach upset, headaches, allergic reactions, or unexplained bleeding. Stop use and speak with your healthcare provider if these symptoms occur.
Key Takeaways: Unlocking the Power of Osteoarthritis Food Supplements
Osteoarthritis food supplements may provide relief and improved mobility.
Evidence varies—choose supplements with strong clinical support.
Consult your healthcare provider before making changes.
Dietary adjustments play a crucial role in joint health.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Osteoarthritis Journey
"Start exploring osteoarthritis food supplements today and discover how you can reclaim mobility, dissolve pain, and restore quality of life—one step at a time."
By combining evidence-based dietary supplements with thoughtful lifestyle changes and medical support, you can unlock new potential in your fight against osteoarthritis.
If you’re seeking even more ways to enhance your joint health and overall mobility, consider exploring additional strategies that go beyond supplements. For those facing persistent discomfort or recovering from procedures, our in-depth guide on solutions for managing pain after total knee replacement offers expert insights and actionable tips. By broadening your approach to arthritis care, you can discover advanced pain management techniques and lifestyle adjustments that support long-term wellness. Take the next step in your journey to better movement and comfort by learning from the latest medical perspectives and patient experiences.
Sources
Exploring the benefits of osteoarthritis food supplements can provide valuable insights into managing joint health. The article “12 Supplements for Osteoarthritis” from the Arthritis Foundation offers a comprehensive overview of various supplements, including glucosamine, chondroitin, and omega-3 fatty acids, detailing their potential effects and safety considerations. (arthritis.org)
Additionally, “5 Supplements to Consider Taking When You Have Arthritis” by EatingWell discusses the roles of omega-3 fatty acids, curcumin, and vitamin D in reducing inflammation and alleviating arthritis symptoms. (eatingwell.com) If you’re serious about enhancing your joint health, these resources will provide you with evidence-based information to make informed decisions.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 


Write A Comment